Question: A saturated vapor stream containing 10.9 mole% propane, 75.2% isobutene, and 13.9% n-butane passes from the top of a distillation column to a total condenser
A saturated vapor stream containing 10.9 mole% propane, 75.2% isobutene, and 13.9% n-butane passes from the top of a distillation column to a total condenser seventy-five percent of the condensate is returned to the column as reflux, and the remainder is removed as the overhead column product at a race of 2500k mol/h. A decision must be made on whether to use a refrigerant or cooling water in the condenser. If the refrigerant is used, it will be fed to the condenser as a liquid and vaporized by the heat released by the condensing column vapor. The refrigerant pressure will be such that the vaporization takes place at ?6?C, at which temperature ?Hv = 151 kJ/kg. The other option calls for cooling water to be taken from a nearby river at its average summer temperature of 25?C. To avoid environmental problems, the temperature of the water returned to the river can be no greater than 34?C. With either system the temperature of the condensate should be 6?C greater than the outlet temperature of the coolant so that if the refrigerant is used the saturated condensate should have a temperature of 0?C, and if cooling water is used the saturated condensate should be at 40?C. The condenser pressure will be set to the minimum value needed to condense all of the vapor, which is to say the condensate will be at its bubble-point temperature at the condenser pressure. Raoult?s law ma? he used for i1 bubble-point and dew-point calculations (see Section 6.4c).
(a) Suppose the refrigerant is used for cooling. Estimate the condenser pressure P (mm Hg): the temperature Tf (?C) of the vapor fed to the condenser, assuming that the vapor is at its de point at pressure P; and the required coolant flow rate (kg/h).
(b) Repeat part (a) assuming that cooling water is fed to the condenser.
(c) What more would you need to know to be able to choose between the two options??
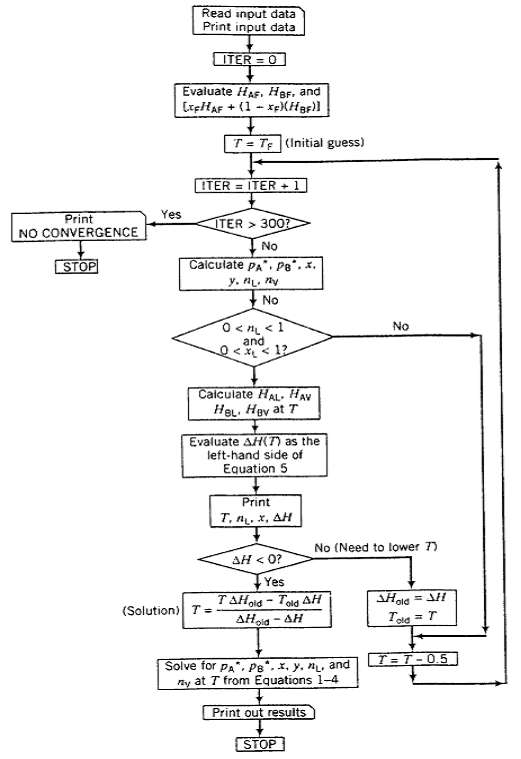
Print NO CONVERGENCE STOP Yes Read input data Print input data ITER = 0 Evaluate HAF, HBF, and [XHAF+ (1-x)(HBF)] T= T (Initial guess) ITER = ITER + 1 ITER > 300? No Calculate PA PB.. F y. L. ny No 0
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Basis 2500 kmol product 1 kmol condensate 25 kmol product h 1090 kmolh C3H8v 7520 kmolhC 4H0 v 1390 ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
13-E-C-E-C-P (475).docx
120 KBs Word File


