Question: Singer Inc. is a retailer operating in Edmonton, Alberta. Singer uses the perpetual inventory method. All sales returns from customers result in the goods being
Singer Inc. is a retailer operating in Edmonton, Alberta. Singer uses the perpetual inventory method. All sales returns from customers result in the goods being returned to inventory. (Assume that the inventory is not damaged.) Assume that there are no credit transactions; all amounts are settled in cash. You are provided with the following information for Singer Inc. for the month of January 2012.
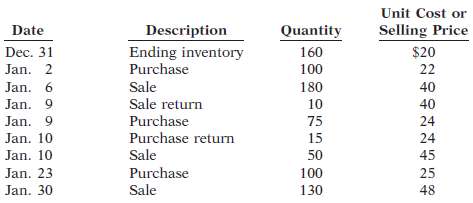
Instructions(a) For each of the following cost flow assumptions, calculate(i) Cost of goods sold,(ii) Ending inventory, and(iii) Gross profit.(1) LIFO. (Assume sales returns had a cost of $20 and purchase returns had a cost of $24.)(2) FIFO. (Assume sales returns had a cost of $20 and purchase returns had a cost of $24.)(3) Moving-average. (Round cost per unit to three decimal places.)(b) Compare results for the three cost flowassumptions.
Unit Cost or Selling Price Date Description Ending inventory Purchase Quantity $20 Dec. 31 160 Jan. 2 100 22 Sale Jan. 6 180 40 Sale return Jan. 9 10 40 Purchase Jan. 9 75 24 Purchase return Jan. 10 15 24 Jan. 10 Sale 50 45 Purchase Jan. 23 100 25 Sale 48 Jan. 30 130
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (183 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Sales Date January 6 180 40 7200 January 9 10 40 400 January 10 50 45 2250 January 30 130 48 6240 ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
48-B-M-A-I (139).docx
120 KBs Word File


