Question: Slow transverse flow around a cylinder (see Fig. 3.7-1). An incompressible Newtonian fluid approaches a stationary cylinder with a uniform, steady velocity v in
Slow transverse flow around a cylinder (see Fig. 3.7-1). An incompressible Newtonian fluid approaches a stationary cylinder with a uniform, steady velocity v∞ in the positive x direction. When the equations of change are solved for creeping flow, the following expressions5 are found for the pressure and velocity in the immediate vicinity of the cylinder (they are not valid at large distances): Here p∞ is the pressure far from the cylinder at y = 0 and with the Reynolds number defined as Re = 2Rv∞p/μ.
(a) Use these results to get the pressure p, the shear stress τrθ, and the normal stress τrr at the surface of the cylinder.
(b) Show that the x-component of the force per unit area exerted by the liquid on the cylinder is
(c) Obtain the force F1, = 2CπLμv∞ exerted in the x direction on a length L of the cylinder.
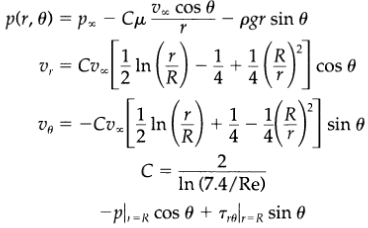
V% Cos 0 p(r, 0) = pz Cu Pgr sin 0 v, = Cv In cos 0 4 1(! 1 R Va = -Cv. In sin 0 4 C = In (7.4/Re) -pl, -R Cos 0 + T,olr=R sin 0
Step by Step Solution
3.37 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Slow transverse flow around a cylinder a At the cylinder surface we get by using Eq B111 P... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
6-E-C-E-T-P (56).docx
120 KBs Word File


