Question: Small diameter electrical heating elements dissipating 50 W/m (length normal to the sketch) are used to heat a ceramic plate of thermal conductivity 2 W/m
Small diameter electrical heating elements dissipating 50 W/m (length normal to the sketch) are used to heat a ceramic plate of thermal conductivity 2 W/m ∙ K. The upper surface of the plate is exposed to ambient air at 30°C with a convection coefficient of 100 W/m2 ∙ K, while the lower surface is well insulated.
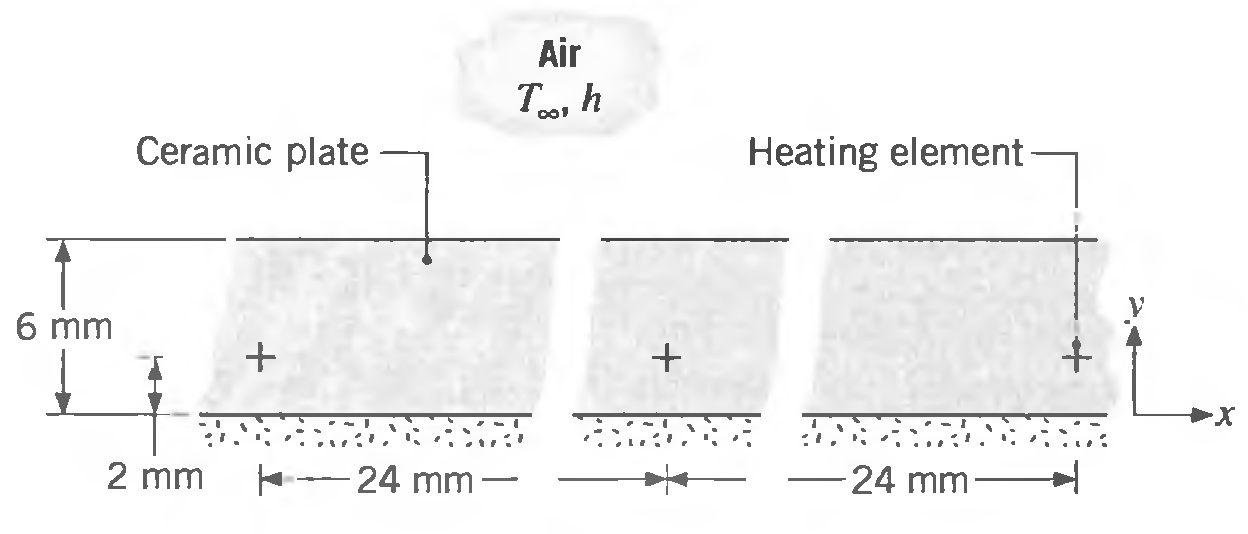
(a) Using the Gauss-Seidel method with a grid spacing of ∆x = 6 mm and ∆y = 2 mm. obtain the temperature distribution within the plate.
(b) Using the calculated nodal temperatures, sketch four isotherms to illustrate the temperature distribution in the plate.
(c) Calculate the heat loss by convection from the plate to the fluid. Compare this value with the element dissipation rate.
(d) What advantage, if any, is there in not making ∆x = ∆y for this situation?
(e) With ∆x = ∆y = 2 mm, calculate the temperature field within the plate and the rate of heat transfer from the plate. Under no circumstances may the temperature at any location in the plate exceed 400°C. Would this limit be exceeded if the air flow were terminated and heat transfer to the air was by natural convection with h = 10W/m2 ∙ K?
Air T, h Ceramic plate Heating element 6 mm X- 2 mm -24 mm -24 mm-
Step by Step Solution
3.52 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
KNOWN Electrical heating elements with known dissipation rate embedded in a ceramic plate of known thermal conductivity lower surface is insulated while upper surface is exposed to a convection proces... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
8-E-M-E-H-M-T (352).docx
120 KBs Word File


