Question: A simplified representation for cooling in very large-scale integration (VLSI) of microelectronics is shown in the sketch. A silicon chip is mounted in a dielectric
A simplified representation for cooling in very large-scale integration (VLSI) of microelectronics is shown in the sketch. A silicon chip is mounted in a dielectric substrate, and one surface of the system is convectively cooled, while the remaining surfaces are well insulated from the surroundings. The problem is rendered two- dimensional by assuming the system to be very long in the direction perpendicular to the paper. Under steady-state operation, electric power dissipation in the chip provides for uniform volumetric heating at a rate of q. However, the heating rate is limited by restrictions on the maximum temperature that the chip is allowed to assume.
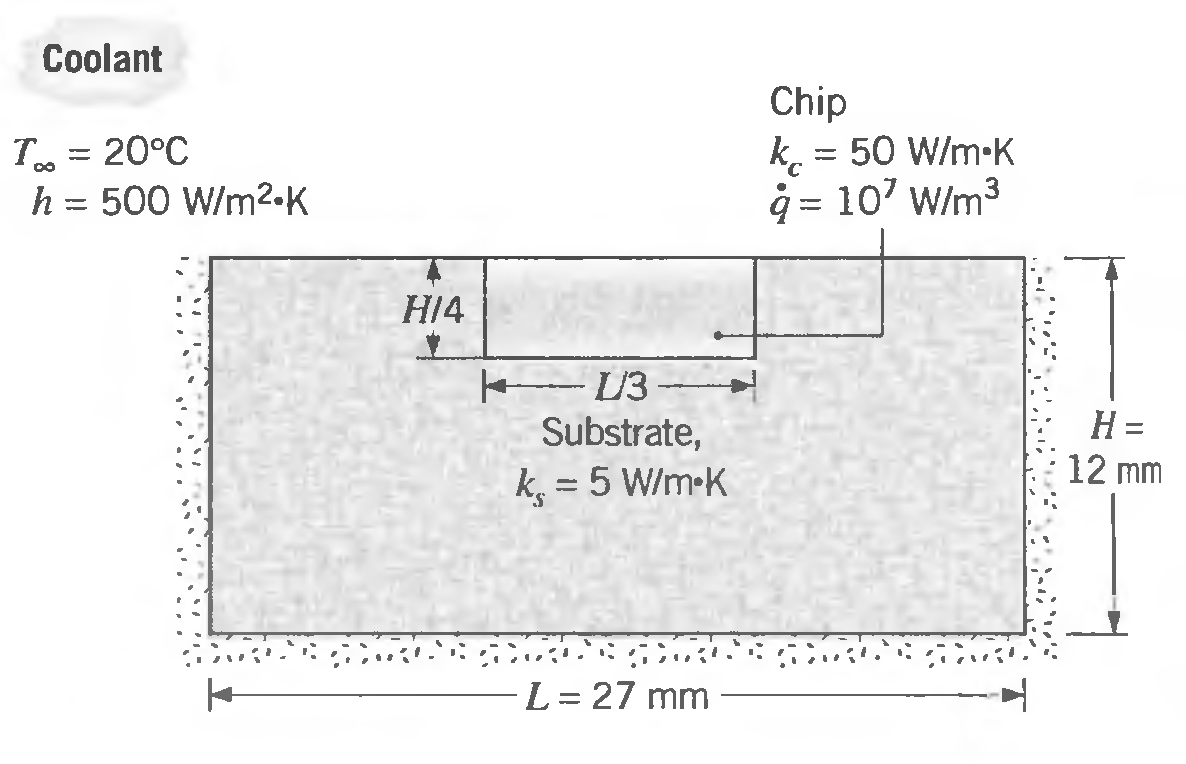
For the conditions shown on the sketch, will the maximum temperature in the chip exceed 85°C, the maximum allowable operating temperature set by industry standards? A grid spacing of 3 mm is suggested.
Coolant Chip k. = 50 W/m-K q = 107 W/m3 T = 20C h = 500 W/m2oK HI4 U3 - Substrate, - %3D 12 mm k, = 5 W/m-K L = 27 mm
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
KNOWN Silicon chip mounted in a dielectric substrate One surface of system is convectively cooled while the remaining surfaces are well insulated FIND Whether maximum temperature in chip will exceed 8... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
8-E-M-E-H-M-T (353).docx
120 KBs Word File


