Question: Kuttas third-order method is defined by y n+1 = y n + 1/6(k 1 + 4k 2 + k * 3 ) with k 1
Table 21.3

Table 21.5
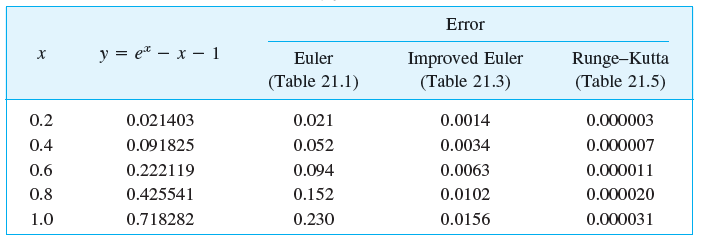
ALGORITHM RUNGE-KUTTA (f, xo, Yo, h, N). This algorithm computes the solution of the initial value problem y' = f(x, y), y(Xx) = Yo at equidistant points X1 = xo + h, x2 = xo + 2h, , XN = xo + Nh; (9) here f is such that this problem has a unique solution on the interval [Xo, Xx] (see Sec. 1.7). INPUT: Function f, initial values xo, Yo, step size h, number of steps N OUTPUT: Approximation yn+1 to the solution y(Xn+1) at xn+1 = xo + (n + 1)h, where n = 0, 1, , N 1 For n = 0, 1, .., N 1 do: ki = hf(xn, Yn) k2 = hf(xn + h, yn + k1) k3 = hf(xn + h, yn + k2) k4 = hf(Xn + h, yn + k3) Xn+1 = Xn + h Yn+1 = Yn + & (k1 + 2k2 + 2k3 + k4) OUTPUT xn+1 Yn+1 End Stop End RUNGE-KUTTA Error y = et x 1 Improved Euler (Table 21.3) Runge-Kutta (Table 21.5) Euler (Table 21.1) 0.000003 0.000007 0.000011 0.2 0.021403 0.091825 0.0014 0.021 0.052 0.094 0.152 0.4 0.0034 0.0063 0.0102 0.6 0.222119 0.425541 0.8 0.718282 0.230 0.0156 0.000020 0.000031 1.0
Step by Step Solution
3.37 Rating (175 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
From y x y and the given formula we get ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


