Question: The trajectory of an object can be modeled as where y = height (m), 0 = initial angle (radians), x = horizontal distance (m),
The trajectory of an object can be modeled as
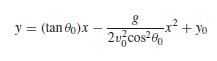
where y = height (m), θ0 = initial angle (radians), x = horizontal distance (m), g = gravitational acceleration (= 9.81 m/s2), v0 = initial velocity (m/s), and y0 = initial height. Use MATLAB to find the trajectories for y0 = 0 and ν0 = 28 m/s for initial angles ranging from 15 to 75° in increments of 15°. Employ a range of horizontal distances from x = 0 to 80 m in increments of 5m. The results should be assembled in an array where the first dimension (rows) corresponds to the distances, and the second dimension (columns) corresponds to the different initial angles. Use this matrix to generate a single plot of the heights versus horizontal distances for each of the initial angles. Employ a legend to distinguish among the different cases, and scale the plot so that the minimum height is zero using the axis command.
y = (tan60)x g 2ucos00 x + yo
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Here is an outline of the MATLAB code to solve the problem described Constants g 981 gravitational a... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


