Question: Section 11.5.4, used the linear associator algorithm to make two vector pair associations. Select three (new) vector pair associations and solve the same task. Test
Section 11.5.4, used the linear associator algorithm to make two vector pair associations. Select three (new) vector pair associations and solve the same task. Test whether your linear associator is interpolative; that is, can it associate near misses of the exemplars? Make your linear associator auto associative.
Data from section 11.5.4
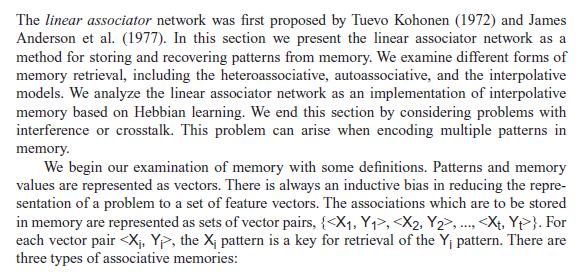

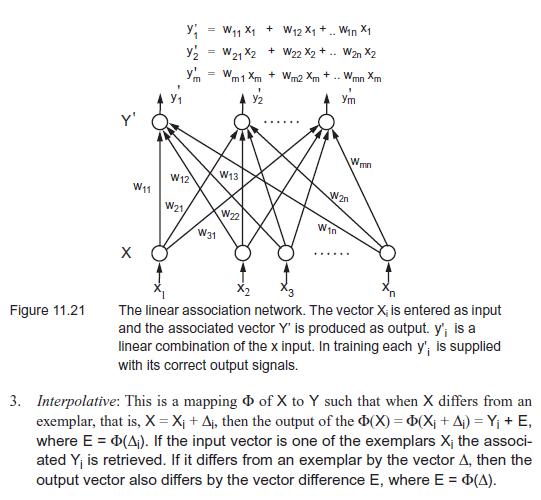
The linear associator network was first proposed by Tuevo Kohonen (1972) and James Anderson et al. (1977). In this section we present the linear associator network as a method for storing and recovering patterns from memory. We examine different forms of memory retrieval, including the heteroassociative, autoassociative, and the interpolative models. We analyze the linear associator network as an implementation of interpolative memory based on Hebbian learning. We end this section by considering problems with interference or crosstalk. This problem can arise when encoding multiple patterns in memory. We begin our examination of memory with some definitions. Patterns and memory values are represented as vectors. There is always an inductive bias in reducing the repre- sentation of a problem to a set of feature vectors. The associations which are to be stored in memory are represented as sets of vector pairs, { , , }. For each vector pair
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Based on the information provided we can outline the steps to create a linear associator that is both autoassociative and interpolative using three ne... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


