Question: W&S Partners commenced planning the Cloud 9 audit by gaining an understanding of the clients structure and its business environment. A major task is to
W&S Partners commenced planning the Cloud 9 audit by gaining an understanding of the client’s structure and its business environment. A major task is to consider the concept of materiality as it applies to the client. The auditor will design procedures in order to identify and correct errors or irregularities that would have a material effect on the financial report and affect the decision making of the users of the financial report. Materiality is used in determining audit procedures and sample selections, and evaluating differences from client records to audit results. It is the maximum amount of misstatement, individually or in aggregate, that can be accepted in the financial report. In selecting the base figure to be used to calculate materiality, an auditor should consider the key drivers of the business. They should ask, ‘What are the end users (that is, shareholders, banks etc.) of the accounts going to be looking at?’ For example, will shareholders be interested in profit figures that can be used to pay dividends and increase share price?
W&S Partners’ audit methodology dictates that one planning materiality (PM) amount is to be used for the financial report as a whole (that is, rather than separate PMs for the income statement and the balance sheet). Further, only one basis should be selected — a blended approach or average should not be used. The basis selected is the one determined to be the key driver of the business.
W&S Partners use the following percentages as starting points for the various bases: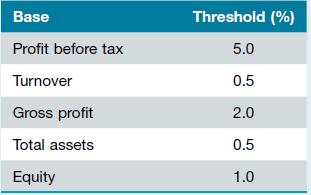
These starting points can be increased or decreased by taking into account qualitative client factors, which could be:
• the nature of the client’s business and industry (for example, rapidly changing, either through growth or downsizing, or an unstable environment)
• if the client is a listed entity (or subsidiary of) subject to regulations • the knowledge of or high risk of fraud.
Typically, profit before tax is used; however, it cannot be used if reporting a loss for the year, if profitability is impacted significantly by ‘one off’ adjustments or transactions, or if the users of the financial report are not basing their investment (or other) decisions on a profit basis.
When calculating PM based on interim figures, it may be necessary to annualise the results. This allows the auditor to plan the audit properly based on an approximate projected year-end balance.
Then, at year-end, the figure is adjusted, if necessary, to reflect the actual results.
Required Using the 30 September 2016 trial balance (in the appendix to this text), calculate planning materiality and include the justification for the basis that you have used for your calculation.
When you are answering the question, you should refer to the information presented for Cloud 9 in the appendix to this text and in the current and earlier chapters. You should also consider your answers to the case study questions in earlier chapters.
PART 2 Analytical procedures Required Answer the following questions based on the information presented for Cloud 9 in the appendix to this text and the current and earlier chapters. You should also consider your answers to the case study questions in earlier chapters.
The trial balance for Cloud 9 as at September 2016 is included in the appendix. Note the following when analysing the company:
The current and non-current assets and liabilities for 31 December 2015 are shown in the balance sheet. In the trial balance, non-current assets are Property, Plant and Equipment, and Deferred Tax. The non-current liabilities are Provisions $110 744 (other Provisions are current liabilities), Interest Bearing Loans — Loan with Bank $850 000 (the remainder of the balance of this account is a current liability), and Provision for Deferred Tax Liabilities $352 231.
Where a ratio requires an average balance and the prior year is not available, use the current year only.
Items of revenue and expense in the trial balance for September 2016 should be annualised where appropriate.
(a) Using analytical procedures and the information provided in the appendix, perform an analysis of Cloud 9’s financial position and its business risks. Discuss the ratios indicating a significant or an unexpected fluctuation.
(b) Which specific areas do you believe should receive special emphasis during your audit? Consider your discussion of the analytical procedures results as well as your preliminary estimate of materiality. Prepare a memorandum to Suzie Pickering outlining potential problem areas (that is, where possible material misstatements in the financial report exist) and any other special concerns (for example, going concern).
Base Profit before tax Turnover Gross profit Total assets Equity Threshold (%) 5.0 0.5 2.0 0.5 1.0
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Performing an analysis of Cloud 9s financial position and business risks using analytical procedures and the provided information 1 Profitability Ratios Gross Profit Margin Calculate gross profit ma... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


