Question: 12. A random variable T is said to have the lognormal( ln, ln) distribution if logT N(ln, 2 ln), where log is the natural
12. A random variable T is said to have the lognormal(
μln, σln) distribution if logT ∼ N(μln, σ2 ln), where log is the natural logarithm. The mean value and variance of T are
![]()
The log-normal(0, 1) distribution is called the standard log-normal distribution.
(a) Show that if T has the log-normal(μln, σln) distribution, its CDF is given by
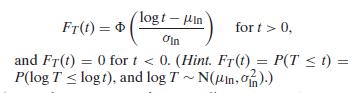
(b) Use the R commands curve(dlnorm(x, 0, 1), 0, 10, col=1, ylab=”Log-Normal PDFs”), curve(dlnorm(x, 1, 1), 0, 10, add=T, col=2), and curve(dlnorm(x, 1.5, 1), 0, 10, add=T, col=3) to superimpose the plots of three log-normal PDFs corresponding to different parameter values. Superimpose the plots of the corresponding three log-normal CDFs by making appropriate changes to these commands (dlnorm changes to plnorm, and PDFs changes to CDFs).
(c) Using the formulas given above, compute the mean and variance of the log-normal(0, 1), log-normal(5, 1)
and log-normal(5, 2) distributions.
(d) The R command qlnorm(0.95), which is equivalent to qlnorm(0.95, 0, 1), gives the 95th percentile of the standard log-normal distribution. Verify that the R commands log(qlnorm(0.95)) and qnorm(0.95) return the same value, which is the 95th percentile of the standard normal distribution, and provide an explanation for this.
HT = en+0/2 0 = 2+ (e% 1).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


