Question: The example on Bayes' Theorem in Section 1.2 concerning the biology of twins was based on the assumption that births of boys arid girls occur
The example on Bayes' Theorem in Section 1.2 concerning the biology of twins was based on the assumption that births of boys arid girls occur equally frequently, and yet it has been known for a very long time that fewer girls are born than boys ( cf. Arbuthnot, 1710). Suppose that the probability of a girl is p, so that
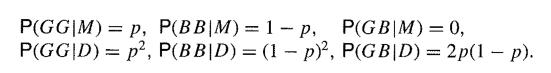
Find the proportion of monozygotic twins in the whole population of twins in terms of p and the sex distribution among all twins.
Bayes' Theorem

P(GG|M)=p, P(BB|M)=1-P, P(GB|M) = 0, P(GG|D) p, P(BB|D) = (1 - p), P(GB|D) = 2p(1 - p). =
Step by Step Solution
3.27 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


