Question: Implement an iterator for the RedBlackTree class in Worked Example 17.2 that visits the nodes in sorted order. Take advantage of the parent links. Data
Implement an iterator for the RedBlackTree class in Worked Example 17.2 that visits the nodes in sorted order. Take advantage of the parent links.
Data from worked example 17.2.



The code for fixing up a double-red violation is quite long. Recall that there are four possible arrangements of the double red nodes:
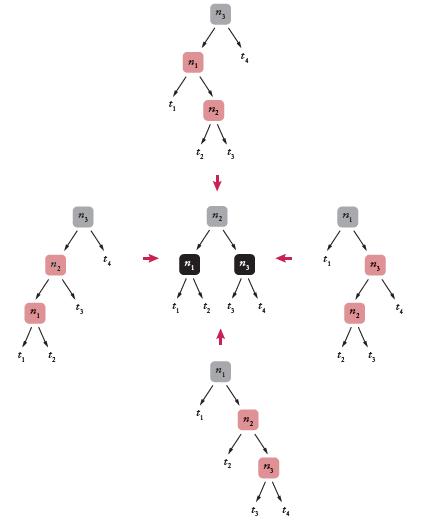
In each case, we must sort the nodes and their children. Once we have the seven references n1, n2, n3, t1, t2, t3, and t4, the remainder of the procedure is straightforward. We build the replacement tree, change the reds to black, and subtract one from the color of the grandparent (which might be a double-black node when this method is called during node removal).
If we find that we introduced another double-red violation, we continue fixing it. Eventually, the violation is removed, or we reach the root, in which case the root is simply colored black:
![]()


WORKED EXAMPLE 17.2 Implementing a Red-Black Tree Problem Statement Implement a red-black tree using the algorithm for adding and removing elements from Section 17.5. Read that section first if you have not done so already. The Node Implementation The nodes of the red-black tree need to store the "color", which we represent as the cost of traversing the node: static final int BLACK = 1; static final int RED = 0; private static final int NEGATIVE RED = -1; private static final int DOUBLE BLACK = 2; static class Mode { public Comparable data; public Node left; public Mode right; public Node parent; public int color; The first two color constants and the Mode class have package visibility. We will add a test class to the same package, which is discussed later in this worked example. Nodes in a red-black tree also have a link to the parent. When adding or moving a node, it is important that the parent and child links are synchronized. Because this synchronization is tedious and error-prone, we provide several helper methods: public class RedBlackTree ( static class Mode {
Step by Step Solution
3.53 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Implementing an iterator for a RedBlack Tree that visits the nodes in sorted order requires an inorder traversal since this type of depthfirst travers... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


