In the Short Takes Example 4.10, suppose that the probability that a medical diagnostic test will give
Question:
In the Short Takes Example 4.10, suppose that the probability that a medical diagnostic test will give a positive result if the disease is not present is reduced from 0.02 to 0.01.
a. If the medical diagnostic test has given a positive result (indicating that the disease is present), what is the probability that the disease is actually present?
b. If the medical diagnostic test has given a negative result (indicating that the disease is not present), what is the probability that the disease is not present?
Example 4.10
Waiting time is a critical issue at fast-food chains, which not only want to minimize the mean service time but also want to minimize the variation in the service time from customer to customer. One fast-food chain carried out a study to measure the variability in the waiting time (defined as the time in minutes from when an order was completed to when it was delivered to the customer) at lunch and breakfast at one of the chain’s stores. The results were as follows: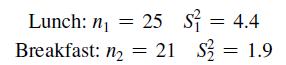
At the 0.05 level of significance, is there evidence that there is more variability in the service time at lunch than at breakfast? Assume that the population service times are normally distributed.
Step by Step Answer:

Business Statistics A First Course
ISBN: 9780135177785
8th Edition
Authors: David M. Levine, Kathryn A. Szabat, David F. Stephan





