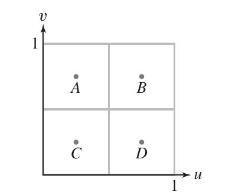
Question: A surface (mathcal{S}) has a parametrization (Phi(u, v)) whose domain (mathcal{D}) is the square in Figure 17. Suppose that (Phi) has the following normal vectors:
A surface \(\mathcal{S}\) has a parametrization \(\Phi(u, v)\) whose domain \(\mathcal{D}\) is the square in Figure 17. Suppose that \(\Phi\) has the following normal vectors:
\[
\begin{array}{ll}
\mathbf{N}(A)=\langle 2,1,0angle, & \mathbf{N}(B)=\langle 1,3,0angle \\
\mathbf{N}(C)=\langle 3,0,1angle, & \mathbf{N}(D)=\langle 2,0,1angle
\end{array}
\]
Estimate \(\iint_{\mathcal{S}} f(x, y, z) d S\), where \(f\) is a function such that \(f(\Phi(u, v))=u+v\).
V B D U
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
We estimate the surface integral by the following Riemann sum iintS fx y z d SDelta ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


