Question: Let (x, y) = (x y)e x . Use the Chain Rule to calculate /u and /v (in terms of u and v), where
Let ƒ(x, y) = (x − y)ex. Use the Chain Rule to calculate ∂ƒ/∂u and ∂ƒ/∂v (in terms of u and v), where x = u − v and y = u + v.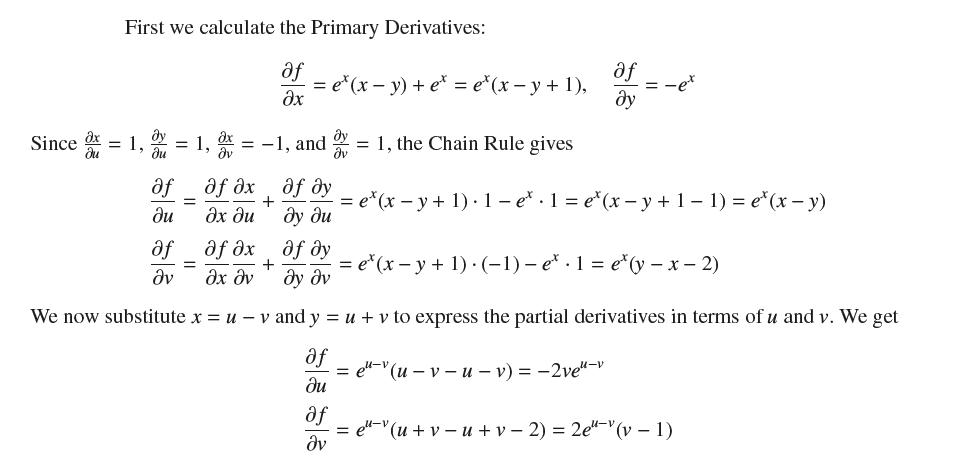
Since x First we calculate the Primary Derivatives: af f = 1, = 1, = -1, and , af = = f x x f + x + = ex(x - y) + e = e*(x-y+1), f f = af v 1, the Chain Rule gives af = -er = ex(x - y + 1) 1-e.1= e(x-y +1 - 1) = e*(x-y) = e*(x - y + 1) . (-1) - e. 1 = e(y - x - 2) We now substitute x = u - v and y = u + v to express the partial derivatives in terms of u and v. We get af = e"-v(u - v - u-v) = -2ve"-v = e"-" (u + v - u + v - 2) = 2e"-(v - 1)
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Since x First we calculate the Primary Derivatives af f 1 1 1 and f ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


