Question: Pappus's Theorem (also called Guldin's Rule), which we introduced in Section 8.4 , states that the area of a surface of revolution (mathcal{S}) is equal
Pappus's Theorem (also called Guldin's Rule), which we introduced in Section 8.4 , states that the area of a surface of revolution \(\mathcal{S}\) is equal to the length \(L\) of the generating curve times the distance traversed by the center of mass. Use Eq. (14) to prove Pappus's Theorem. If \(C\) is the graph \(z=g(y)\) for \(c \leq y \leq d\), then the center of mass is defined as the point \((\bar{y}, \bar{z})\) with
\[
\bar{y}=\frac{1}{L} \int_{C} y d s, \quad \bar{z}=\frac{1}{L} \int_{C} z d s
\]
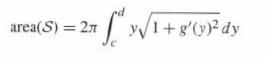
area(S) = 27 y/1+g'(y) dy
Step by Step Solution
3.34 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
We may assume that the generating curve zgy lies in the region y geq 0 otherwise we translate the ax... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


