Question: Use Green's Theorem to evaluate the line integral. Orient the curve counterclockwise unless otherwse indicated. Let (mathbf{F}(x, y)=leftlangle 2 x e^{y}, x+x^{2} e^{y}ightangle) and let
Use Green's Theorem to evaluate the line integral. Orient the curve counterclockwise unless otherwse indicated.
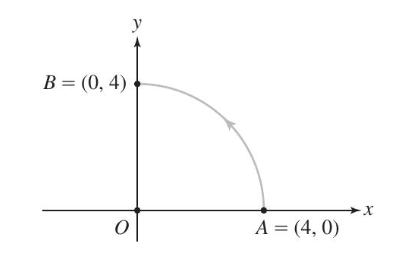
Let \(\mathbf{F}(x, y)=\left\langle 2 x e^{y}, x+x^{2} e^{y}ightangle\) and let \(C\) be the quarter-circle path from \(A\) to \(B\) in Figure 18. Evaluate \(I=\oint_{C} \mathbf{F} \cdot d \mathbf{r}\) as follows:
(a) Find a function \(f(x, y)\) such that \(\mathbf{F}=\mathbf{G}+abla f\), where \(\mathbf{G}=\langle 0, xangle\).
(b) Show that the line integrals of \(\mathbf{G}\) along the segments \(\overline{O A}\) and \(\overline{O B}\) are zero.
(c) Evaluate I. Use Green's Theorem to show that
\[
I=f(B)-f(A)+4 \pi
\]
THEOREM 1 Green's Theorem Let D be a domain whose boundary 3D is a simple closed curve, oriented counterclockwise. If F and F have continuous partial deriva- tives in an open region containing D, then $o F1 dx + F2 dy 1 (F2-F) da dA = ay 2
Step by Step Solution
3.30 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a We need to find a potential function fx y for the difference mathbfFmathbfGleftlangle 2 x ey xx2 e... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


