Question: Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the surface integral S F ds; that is, calculate the flux of F across S. F(x, y,
Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the surface integral ∫∫S F · ds; that is, calculate the flux of F across S.
F(x, y, z) = x2z3 i + 2xyz3j + xz4k, S is the surface of the box with vertices (±1, ±2, ±3)
Data from the Divergence Theorem
Let E be a simple solid region and let S be the boundary surface of E, given with positive (outward) orientation. Let F be a vector field whose component functions have continuous partial derivatives on an open region that contains E. Then
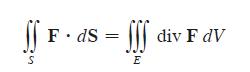
S F. dS SSS E div F dV
Step by Step Solution
3.24 Rating (168 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To calculate the surface integral S F dS the flux of F across the surface S you can use the Divergen... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


