Question: A diagnostic test is designed to detect whether subjects have a certain disease. A positive test outcome predicts that a subject has the disease. Given
A diagnostic test is designed to detect whether subjects have a certain disease. A positive test outcome predicts that a subject has the disease. Given that the subject has the disease, the probability the diagnostic test is positive is called the sensitivity. Given that the subject does not have the disease, the probability the test is negative is called the specificity. Consider the 2 x 2 table having the true status as the row riable and the diagnosis as the column variable. of each classification, then sensitivity is and specificity is 12. Let y denote the probability that a subject has the disease.
a. Given that the diagnosis is positive, use Bayes Theorem to show that the probability a subject truly has the disease is 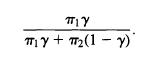
b. Suppose a diagnostic test for HIV+ status has sensitivity and specificity both equal to .95. If y = .005, find the probability that a subject is HIV+, given that the diagnostic test is positive.
c. To better understand the answer in (b), find the four joint probabilities for the 2 2 table, and discuss their relative sizes.
TY Tuy+ m(1 - 1)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


