Develop a Gibbs-Duhem equation for strong electrolyte-water systems, and use this equation and the data in Illustration
Question:
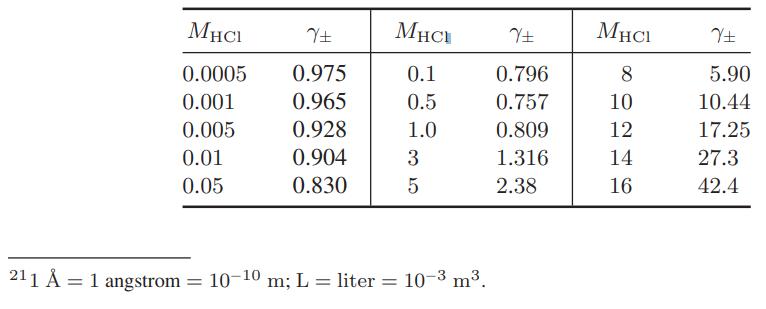
Develop a Gibbs-Duhem equation for strong electrolyte-water systems, and use this equation and the data in Illustration 9.10-1 to compute the activity coefficient of water in aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions at 25°C.
Illustration 9.10-1
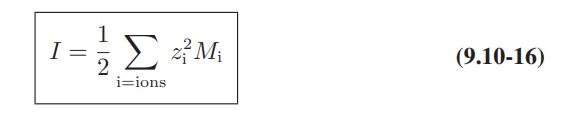
Use of Electrolyte Solution Models The data below are for the activity coefficients of HCl in aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions as a function of HCl molality at 25°C. Compare the predictions of the Debye-Huckel model (Eqs. 9.10-15 and 9.10-16), and the extended Debye-Huckel models (Eqs. 9.10-17 and 9.10-18) with these data.
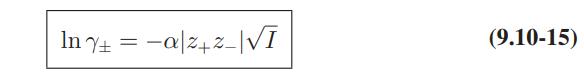
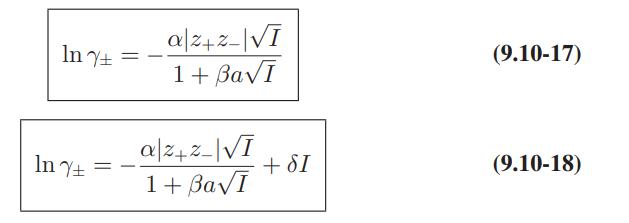
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Chemical Biochemical And Engineering Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9780470504796
5th Edition
Authors: Stanley I. Sandler
Question Posted: