Question: Topic 6C discusses the relationship between molecular structure and the strengths of acids. The same ideas can be applied to bases. (a) Explain the relative
Topic 6C discusses the relationship between molecular structure and the strengths of acids. The same ideas can be applied to bases.
(a) Explain the relative strengths of the Brønsted bases OH–, NH2 –, and CH3 – (see Table 6C.3).
(b) Explain why NH3 is a weak base in water, but PH3 forms essentially neutral solutions.
(c) If you were ranking the species in (a) or (b) as Lewis bases, would your rankings be the same or different? Explain your reasoning.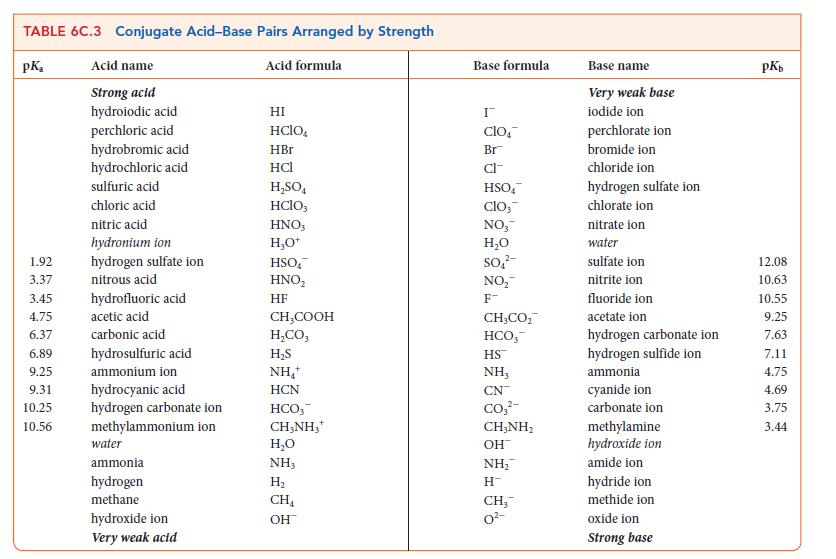
TABLE 6C.3 Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs Arranged by Strength pK Acid name Acid formula Strong acid hydroiodic acid perchloric acid hydrobromic acid hydrochloric acid sulfuric acid chloric acid nitric acid hydronium ion hydrogen sulfate ion nitrous acid 1.92 3.37 3.45 4.75 6.37 6.89 hydrosulfuric acid 9.25 ammonium ion 9.31 hydrocyanic acid 10.25 hydrogen carbonate ion 10.56 methylammonium ion hydrofluoric acid acetic acid carbonic acid water ammonia hydrogen methane hydroxide ion Very weak acid HI HCIO. HBr HCI HSO4 HClO3 HNO3 HO+ HSO HNO HF CHCOOH H,CO, HS NH+ HCN HCO, CH3NH3* HO NH3 H CH OH Base formula I clo Br CI- HSO clo, NO HO SO NO F- CH,CO, HCO, HS NH, CN CO3- CH,NH, OH NH H CH3 0- Base name Very weak base iodide ion perchlorate ion bromide ion chloride ion hydrogen sulfate ion chlorate ion nitrate ion water sulfate ion nitrite ion fluoride ion acetate ion hydrogen carbonate ion hydrogen sulfide ion ammonia cyanide ion carbonate ion methylamine hydroxide ion amide ion hydride ion methide ion oxide ion Strong base pKb 12.08 10.63 10.55 9.25 7.63 7.11 4.75 4.69 3.75 3.44
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The relative strengths of the Brnsted bases OH NH2 and CH3 can be explained by their ability to donate a pair of electrons to form a bond with an H ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


