A benzene solution and a water solution of acetic acid (CH 3 CO 2 H; molar mass
Question:
A benzene solution and a water solution of acetic acid (CH3CO2H; molar mass = 60.05 g/mol) are both 0.50 mass percent acid. The freezing-point depression of the benzene solution is 0.205 °C, and that of the aqueous solution is 0.159 °C.
(a) Using the freezing-point depression constants in Table 12.4, calculate the molality of the solute in each of the two solutions.
(b) What are the van’t Hoff factors for the water solution and benzene solution from these experiments?
(c) Note the difference between the van’t Hoff factors, and offer an explanation for the experimental results.
Table 12.4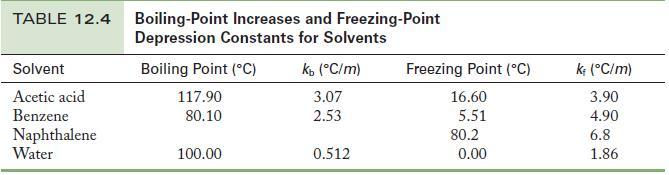
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Chemistry Principles And Practice
ISBN: 9780534420123
3rd Edition
Authors: Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball
Question Posted:





