Question: Accelerators such as the Triangle Universities Meson Facility (TRIUMF) in British Columbia produce secondary beams of pions by having an intense primary proton beam strike
Accelerators such as the Triangle Universities Meson Facility (TRIUMF) in British Columbia produce secondary beams of pions by having an intense primary proton beam strike a target. Such “meson factories” have been used for many years to study the interaction of pions with nuclei and, hence, the strong nuclear force. One reaction that occurs is ![]() where the Δ++ is a very short-lived particle. The graph in Figure 33.26 shows the probability of this reaction as a function of energy. The width of the bump is the uncertainty in energy due to the short lifetime of the Δ++ .
where the Δ++ is a very short-lived particle. The graph in Figure 33.26 shows the probability of this reaction as a function of energy. The width of the bump is the uncertainty in energy due to the short lifetime of the Δ++ .
(a) Find this lifetime.
(b) Verify from the quark composition of the particles that this reaction annihilates and then re-creates a d quark and a d̅ antiquark by writing the reaction and decay in terms of quarks.
(c) Draw a Feynman diagram of the production and decay of the Δ++ showing the individual quarks involved.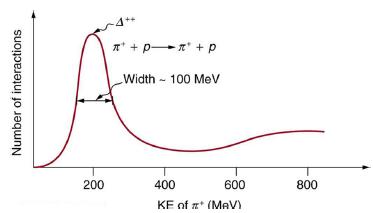
++PA+++ +p=
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step 1 To determine a The life time of A particle created at TRIUMF Step 2 Answer The life time of 4 ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


