Question: Repeat the seesaw problem in Example 9.1 with the center of mass of the seesaw 0.160 m to the left of the pivot (on the
Repeat the seesaw problem in Example 9.1 with the center of mass of the seesaw 0.160 m to the left of the pivot (on the side of the lighter child) and assuming a mass of 12.0 kg for the seesaw. The other data given in the example remain unchanged. Explicitly show how you follow the steps in the Problem-Solving Strategy for static equilibrium.
Data given in Example 9.1
The two children shown in Figure 9.8 are balanced on a seesaw of negligible mass. (This assumption is made to keep the example simple—more involved examples will follow.) The first child has a mass of 26.0 kg and sits 1.60 m from the pivot.
(a) If the second child has a mass of 32.0 kg, how far is she from the pivot?
(b) What is FP, the supporting force exerted by the pivot?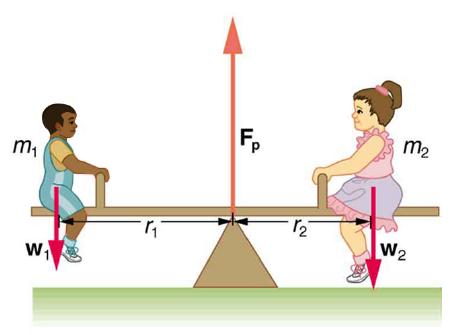
Strategy
Both conditions for equilibrium must be satisfied. In part (a), we are asked for a distance; thus, the second condition (regarding torques) must be used, since the first (regarding only forces) has no distances in it. To apply the second condition for equilibrium, we first identify the system of interest to be the seesaw plus the two children. We take the supporting pivot to be the point about which the torques are calculated. We then identify all external forces acting on the system.
m W Fp 12 m W
Step by Step Solution
3.32 Rating (143 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Given m1 260 kg m2 320 kg ms 120 kg r1 160 m rs 0160 m find a r2 b Fp a S... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


