Question: Hold down is another distance-vector loop avoidance technique, whereby hosts ignore updates for a period of time until link failure news has had a chance
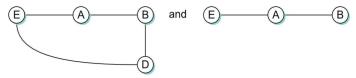
Hold down is another distance-vector loop avoidance technique, whereby hosts ignore updates for a period of time until link failure news has had a chance to propagate. Consider the networks in Figure 3.55, where all links have cost 1 except E–D with cost 10.
Suppose that the E–A link breaks and B reports its loop-forming E route to A immediately afterwards (this is the false route, via A).
Specify the details of a hold-down interpretation, and use this to describe the evolution of the routing loop in both networks. To what extent can hold-down prevent the loop in the EAB network without delaying the discovery of the alternative route in the EABD network?
Figure 3.55)
(E) (A) B (D and (E) (A) B
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Holddown is a mechanism used in distancevector routing protocols to prevent routing loops After a router detects that a directly connected link has failed it will mark the route as unreachable in its ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


