Question: Figure 12.5 demonstrates a concurrent server in which the parent process creates a child process to handle each new connection request. Trace the value of
Figure 12.5 demonstrates a concurrent server in which the parent process creates a child process to handle each new connection request. Trace the value of the reference counter for the associated file table for Figure 12.5.
Figure 12.5
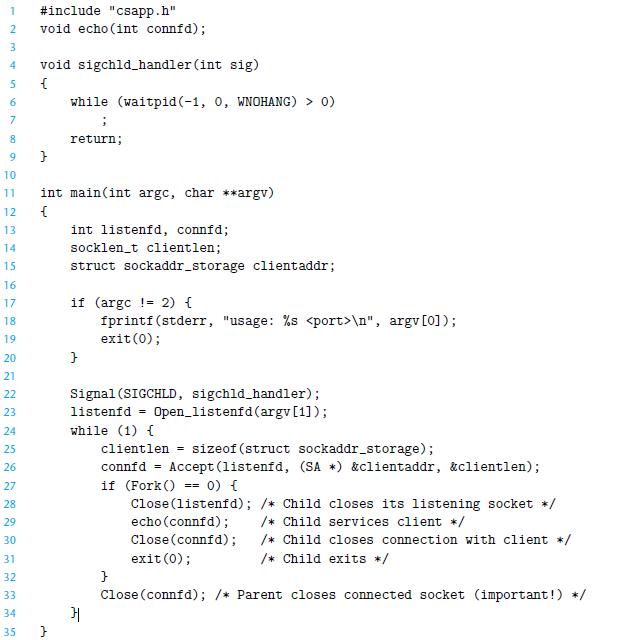
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include "csapp.h" void echo(int connfd); void sigchld_handler (int sig) { } while (waitpid (-1, 0, WNOHANG) > 0) ; return; int main(int argc, char **argv) { } int listenfd, connfd; socklen_t clientlen; struct sockaddr_storage clientaddr; if (argc ! 2) { fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s ", argv[0]); exit(0); } Signal (SIGCHLD, sigchld_handler); listenfd = Open_listenfd (argv[1]); while (1) { clientlen sizeof (struct sockaddr_storage); }| connfd = Accept (listenfd, (SA) &clientaddr, &clientlen); if (Fork () == == 0) { Close (listenfd); /* Child closes its listening socket */ echo (connfd); /* Child services client */ Close (connfd); exit(0); /* Child closes connection with client */ /* Child exits */ } Close (connfd); /* Parent closes connected socket (important!) */
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
When the parent process on the concurrent server starts executing the reference counter ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


