Question: The getaddrinfo and getnameinfo functions subsume the functionality of inet_pton and inet_ntop, respectively, and they provide a higher-level of abstraction that is independent of any
The getaddrinfo and getnameinfo functions subsume the functionality of inet_pton and inet_ntop, respectively, and they provide a higher-level of abstraction that is independent of any particular address format. To convince yourself how handy this is, write a version of HOSTINFO (Figure 11.17) that uses inet_pton instead of getnameinfo to convert each socket address to a dotted-decimal address string.
Figure 11.17
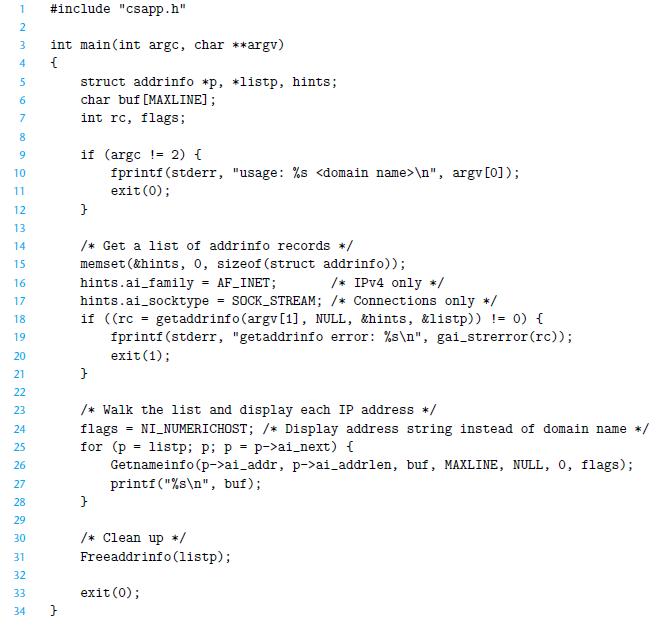
1 #include "csapp.h" 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 int main(int argc, char **argv) { } struct addrinfo *p, listp, hints; char buf [MAXLINE]; int rc, flags; if (argc ! 2) { fprintf (stderr, "usage: %s ", argv [0]); exit(0); } /* Get a list of addrinfo records */ memset(&hints, 0, sizeof (struct addrinfo)); hints.ai_family = AF_INET; /* IPv4 only */ hints. ai_socktype SOCK_STREAM; /* Connections only */ if ((rc = getaddrinfo (argv[1], NULL, &hints, &listp)) != 0) { fprintf (stderr, "getaddrinfo error: %s ", gai_strerror(rc)); exit (1); } /* Walk the list and display each IP address */ flags NI_NUMERICHOST; /* Display address string instead of domain name */ for (p } = = = listp; p: P = p->ai_next) { Getnameinfo (p->ai_addr, p->ai_addrlen, buf, MAXLINE, NULL, 0, flags); printf ("%s ", buf); /* Clean up */ Freeaddrinfo (listp); exit (0);
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Heres a solution Notice how much more difficult it is to use inetntop which requires messy ca... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


