Alexander Mann Solutions (AMS) provides Recruitment Process Outsourcing (RPO) and consultancy services to 45 major clients. They
Question:
Alexander Mann Solutions (AMS) provides Recruitment Process Outsourcing (RPO) and consultancy services to 45 major clients. They were the first to introduce the concept of RPO in 1996 and are now the leading global provider of these services employing approximately 1,500 people. They have won a series of awards over the years, most recently the HROA Baker’s Dozen Customer Satisfaction Award.
Mission and structure
AMS provides talent and resourcing capability for organizations, based on the shared belief that people are the foundation for success. They deliver this through innovative and measurable outsourcing and consulting services. In practice, the services provided can be grouped into three areas:
l Outsourced recruitment and selection services;
l Management of internal resourcing and contingent workforces;
l Consulting advice in areas such as employer branding, external and internal resourcing, talent management, executive search and outplacement and redeployment.
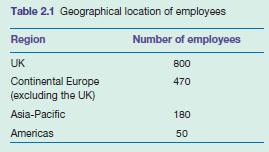
They provide these services to clients in various sectors including: Investment Banking, Retail Banking & Financial Services, Consulting Services, IT & Telco, Healthcare, Defense & Engineering and FMCG. The geographical breakdown of numbers of employees is as follows:
Employees are located on one of four sites (see Figure 2.6):
Figure 2.6
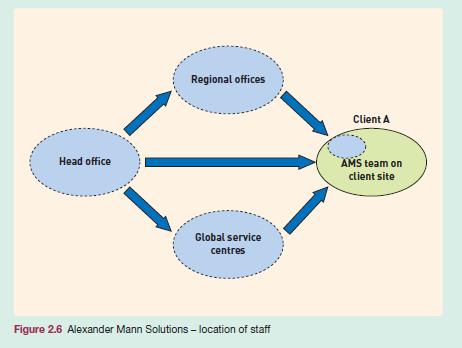
l Client sites providing day-to-day recruitment and selection services, where about 40 per cent of their employees are located;
l G lobal Services Centers (in Krakow, UK, Manila and Cleveland, OH) providing extensive back-office services such as security checks and organizing interview schedules and assessment centers (15 per cent of the workforce);
l Regional Offices providing recruitment and selection services to clients (39 per cent of the workforce);
l U K office central functions including HR, resourcing, finance, commercial, legal, marketing facilities and technology (6 per cent of the workforce).
A very high proportion of AMS staff are therefore working for clients either directly or indirectly. AMS employees based on client sites are working alongside client staff on a daily basis and are surrounded by their branding. One client-based senior manager said, ‘You are pretty much totally immersed with the client. Everything about your employment, bar your pay packet, is client-focused, your business card, your laptop, your client office. My contact with the world outside of (the client) is minimal.’ The risk here is that AMS employees may become more committed to their client than to their employer. Indeed, in some instances AMS can seem very remote and abstract.
Role types
The following roles are typically found within each of the client teams:
l Head of Client Services – has overall responsibility for relationships and delivery of all resourcing services to one or more clients;
l Manager – is responsible for the day-to-day management of the client relationship and service delivery;
l Principal Specialist – responsible for delivering dayto-
day services to hiring managers and dealing with candidates.
l Specialist – is involved in the day-to-day resourcing activities for the client;
l Administrator/Coordinator – provides back-up and support to the Specialist and Principal Specialists.
Client teams can vary in size from over 100 people for a large account to just two or three for a smaller one.
People Strategy
The People Strategy seeks to make the employee value proposition of ‘inspiring people’ a reality for all employees. In particular the People Capital specialists aim to support the AMS vision and mission by driving business transformation and delivering operational excellence through the provision of innovative global programmers. In particular the key priorities are to create a high-performance culture within AMS by:
l Creating a positive and inclusive environment;
l Strengthening the leadership capability;
l Identifying and nurturing talent;
l Rewarding achievement and delivering high performance;
l Making a positive difference to global and local communities;
l Ensuring flexibility and choice.
People capital structure
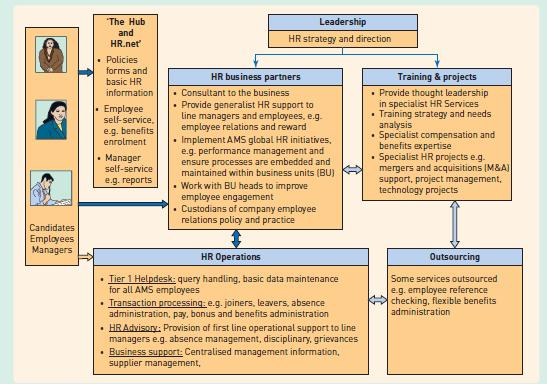
There is a global team, based in six territories (UK, US, Australia, Poland, Philippines, China) of approximately 20 HR and training professionals. The HR Business Partner (HRBP) model is adopted, with the HRBP providing specific sector or geography specific support, who are in turn supported by an HR operations team (administration, technology, reporting etc.), as shown below. Most of the Operations support is provided from Poland and the Philippines.
Particular emphasis is given to the professional development of AMS employees. Indeed, the firm facilitates professional development by encouraging employees to move between different clients on a regular basis – typically after two years with a client. This is designed to allow employees to learn new skills, acquire knowledge about a range of sectors and add well-known brands to their CV. One client manager said, ‘without ever having to jump into another organization I am getting the exposure and contacts, and just working with clients in different industries is quite rare’. Another more junior client-based employee said, ‘I have had variety …you might work on something for 6 months and then it is something else, you always feel as if you are doing something a bit different.’ While a team manager commented that ‘There is always the opportunity to
take yourself off one client site and go and work another site, so that was always a big draw for me, the fact that I am part of a bigger organization that has other opportunities.’
This also has benefits for clients because they have the benefit of staff who have a range of experiences upon which they can draw and these staff themselves have a network of talent that they can consult if a difficult problem emerges...........
Question
1 What are the main challenges faced by AMS when seeking to strengthen employee commitment to the organization?
2 Consider the possible actions that AMS might have made to strengthen organisational commitment?
3 Why have AMS made the changes, as detailed in the case, to their HR practices?
4 What evidence is there that these changes have had a positive influence on organizational performance?
Step by Step Answer:

Contemporary Human Resource Management Text And Cases
ISBN: 9780273757825
4th Edition
Authors: Tom Redman, Adrian Wilkinson




