Question: Using the Penn World Table exchange rates in Stata (webuse pennxrate): (a) Perform the LLC panel unit root tests for (ln) (exchange rates) for OECD
Using the Penn World Table exchange rates in Stata (webuse pennxrate):
(a) Perform the LLC panel unit root tests for \(\ln\) (exchange rates) for OECD countries with trend and without trend. This can be done using the command xtunitroot llc lnrxrate if oecd, lags(aic 10) kernel(bartlett nwest) trend.
(b) Perform the Harris and Tzavalis panel unit root tests for \(\ln\) (exchange rates) for OECD countries with trend and without trend. This can be done using the command xtunitroot ht lnrxrate if oecd, demean trend.
(c) Perform the IPS panel unit root tests for \(\ln\) (exchange rates) for OECD countries with trend and without trend. This can be done using the command xtunitroot ips lnrxrate if oecd, lags(aic 3) trend.
(d) Perform the Breitung panel unit root tests for \(\ln\) (exchange rates) for OECD countries with trend and without trend. This can be done using the command xtunitroot breitung lnrxrate if oecd, lags(3) robust trend.
(e) Perform the combining \(p\)-values Fisher panel unit root tests for \(\ln\) (exchange rates) for OECD countries with trend and without trend. This can be done using the command xtunitroot fisher lnrxrate if oecd, dfuller lags(3) trend.
(f) Perform the Hadri panel stationarity tests for \(\ln\) (exchange rates) for OECD countries with trend and without trend. This can be done using the command xtunitroot hadri lnrxrate if oecd, kernel(bartlett) trend.
(g) Compute the average correlation coefficients and Pesaran's CD test for \(\ln\) (exchange rates) for OECD countries. This can be done using the command xtcd lnxrate if oecd.
(h) Perform the Maddala and Wu (1999) and Pesaran (2007) CIPS panel unit root tests for \(\ln\) (exchange rates) for OECD countries with trend and without trend. This can be done using the Stata command multipurt lnrxrate if oecd, \(\operatorname{lags}(3)\).
Penn World Table:
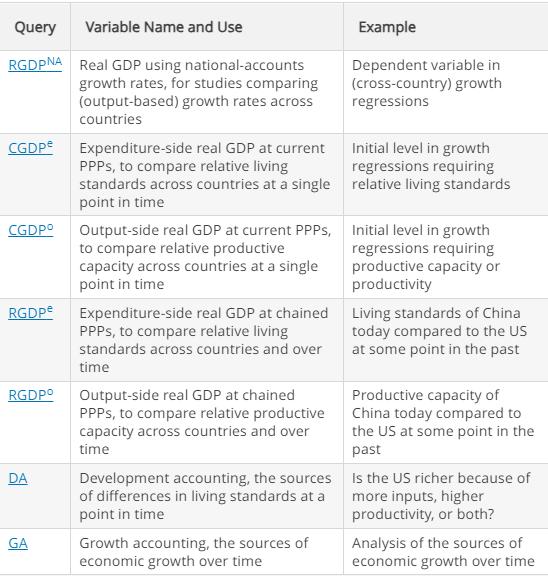
Query Variable Name and Use RGDPNA Real GDP using national-accounts growth rates, for studies comparing (output-based) growth rates across countries CGDPe CGDP RGDPe RGDP DA GA Expenditure-side real GDP at current PPPs, to compare relative living standards across countries at a single point in time Output-side real GDP at current PPPS, to compare relative productive capacity across countries at a single point in time Expenditure-side real GDP at chained PPPs, to compare relative living standards across countries and over time Output-side real GDP at chained PPPS, to compare relative productive capacity across countries and over time Development accounting, the sources of differences in living standards at a point in time Growth accounting, the sources of economic growth over time Example Dependent variable in (cross-country) growth regressions Initial level in growth regressions requiring relative living standards Initial level in growth regressions requiring productive capacity or productivity Living standards of China today compared to the US at some point in the past Productive capacity of China today compared to the US at some point in the past Is the US richer because of more inputs, higher productivity, or both? Analysis of the sources of economic growth over time
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


