Consider the three deformation cases of simple tension, pure shear, and hydrostatic compression as discussed in Section
Question:
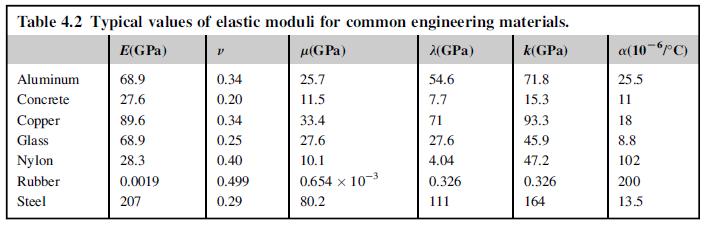
Consider the three deformation cases of simple tension, pure shear, and hydrostatic compression as discussed in Section 4.3 . Using the nominal values from Table 4.2 , calculate the resulting strains in each of these cases for:
a. ![]()
b. ![]()
c. ![]()
Note that for aluminum and steel, these tensile and shear loadings are close to the yield values of the material.
Table 4.2
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Elasticity Theory Applications And Numerics
ISBN: 9780128159873
4th Edition
Authors: Martin H. Sadd Ph.D.
Question Posted:





