Question: As pointed out in the Process Description, the watergas shift reaction (Equation 13.2) occurs in the reformer along with the reforming reaction (Equation 13.1). It
As pointed out in the Process Description, the water–gas shift reaction (Equation 13.2) occurs in the reformer along with the reforming reaction (Equation 13.1). It too is controlled by chemical equilibrium.
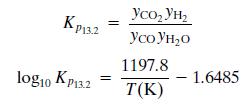
where the nomenclature is analogous to that in the preceding problem.
a. Taking into account the occurrence of reactions given by both Equations 13.1 and 13.2, estimate the composition of the product gas leaving the reformer and the conversion of CH4, assuming the product stream leaving the reformer has achieved chemical equilibrium at 855°C and 1.6 MPa. What is the total flow rate of this stream in both kmol/h and kg/h? What effect does the water gas shift reaction have on the production of CO at the reformer conditions?
b. The ratio of CO to H2 can be an important variable in efficient use of raw materials. In this case study a 3:1 steam-to-methane molar ratio of feed streams was specified. Determine how this feed ratio affects the ratio of CO to H2 in the product from the reformer assuming the reaction products are in chemical equilibrium at 855°C and 1.6 MPa.
Equation 13.1
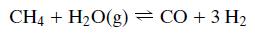
Equation 13.12
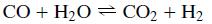
, , P13.2 , 1197.8 log1o KP13.2 -1.6485 T(K)
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a To estimate the composition of the product gas leaving the reformer and the conversion of CH4 we n... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


