Question: Shown here are the abstract and two tables from a research study entitled Adult Children of Alcoholics: Are They at Greater Risk for Negative Health
Shown here are the abstract and two tables from a research study entitled “Adult Children of Alcoholics: Are They at Greater Risk for Negative Health Behaviors?” by Arlene E. Hall. Based on the abstract and the tables, answer these questions.
1. What was the purpose of the study?
2. How many groups were used in the study?
3. By what means were the data collected?
4. What was the sample size?
5. What type of sampling method was used?
6. How might the population be defined?
7. What may have been the hypothesis for the ANOVA part of the study?
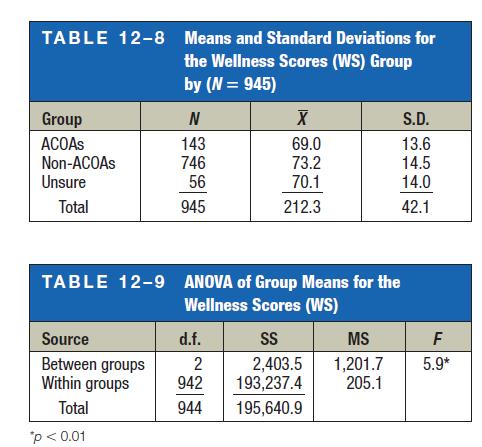
8. Why was the one-way ANOVA procedure used, as opposed to another test, such as the t test?
9. What part of the ANOVA table did the conclusion “ACOAs had significantly lower wellness scores (WS) than non-ACOAs” come from?
10. What level of significance was used?
11. In the following excerpts from the article, the researcher states that
. . . using the Tukey-HSD procedure revealed a significant difference between ACOAs and non- ACOAs, p = 0.05, but no significant difference was found between ACOAs and Unsures or between non-ACOAs and Unsures.
Using Tables 12–8 and 12–9 and the means, explain why the Tukey test would have enabled the researcher to draw this conclusion.
Abstract The purpose of the study was to examine and compare the health behaviors of adult children of alcoholics (ACOAs) and their non-ACOA peers within a university population. Subjects were 980 undergraduate students from a major university in the East. Three groups (ACOA, non-ACOA, and Unsure) were identified from subjects’ responses to three direct questions regarding parental drinking behaviors. A questionnaire was used to collect data for the study. Included were questions related to demographics, parental drinking behaviors, and the College Wellness Check (WS), a health risk appraisal designed especially for college students (Dewey & Cabral, 1986). Analysis of variance procedures revealed that ACOAs had significantly lower wellness scores (WS) than non-ACOAs. Chi-square analyses of the individual variables revealed that ACOAs and non-ACOAs were significantly different on 15 of the50 variables of the WS. A discriminant analysis procedure revealed the similarities between Unsure subjects and ACOA subjects. The results provide valuable information regarding ACOAs in a nonclinical setting and contribute to our understanding of the influences related to their health risk behaviors.
TABLE 12-8 Means and Standard Deviations for the Wellness Scores (WS) Group by (N = 945) Group ACOAS Non-ACOAS Unsure Total Source Between groups Within groups Total N 143 746 56 945 *p
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (171 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 The purpose of the study was to examine and compare the health behaviors of adult children of alco... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


