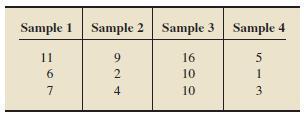
Question: We provide data from independent simple random samples from several populations. In each case, a. Compute SST, SSTR, and SSE by using the computing formulas
We provide data from independent simple random samples from several populations. In each case,
a. Compute SST, SSTR, and SSE by using the computing formulas given in Formula 13.1
b. Compare your results in part (a) for SSTR and SSE, where you employed the defining formulas.
c. Construct a one-way ANOVA table.
d. Decide, at the 5% significance level, whether the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the means of the populations from which the samples were drawn are not all the same.
FORMULA 13.1
For a one-way ANOVA of k population means, the defining and computing formulas for the three sums of squares are as follows.

In this table, we used the notation
nj = total number of observations
x̄j = mean of all n observations ;
and, for j = 1, 2, . . . , k
Note that a summation involving a subscript i is over all n observations; one involving a subscript j is over the k populations.
Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 2 11 6 7 626 9 2 4 Sample 3 Sample 4 16 10 10 5 1 3
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
We have the following a Consequently b c d The df are 38 The critica... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


