Music-Is-Us, Inc., is a supplier of musical instruments for professional and amateur musicians. The companys accountants make
Question:
Music-Is-Us, Inc., is a supplier of musical instruments for professional and amateur musicians. The company’s accountants make adjusting entries monthly, and they make all closing entries annually. The company is growing rapidly and prides itself on having no long-term liabilities.
The company has provided the following trial balance dated December 31, 2015:
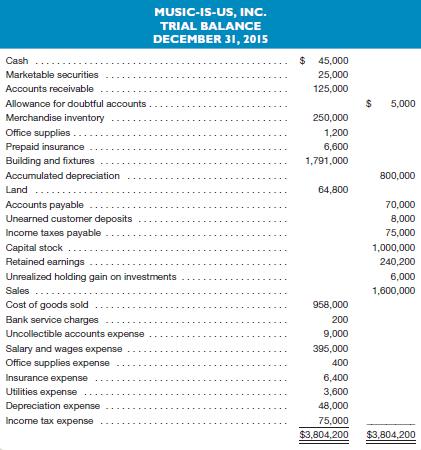
Other information pertaining to the company’s trial balance is shown below:
1. The most recent bank statement reports a balance of $46,975. Included with the bank statement was a $2,500 check from Iggy Smarts, a professional musician, charged back to Music-Is-Us as NSF. The bank’s monthly service charge was $25. Three checks written by Music-Is-Us to suppliers of merchandise inventory had not yet cleared the bank for payment as of the statement date. These checks included: no. 508, $5,500; no. 511, $7,500; and no. 521, $8,000. Deposits of $16,500 reached the bank too late for inclusion in the current bank statement. The company prepares a bank reconciliation at the end of each month.
2. Music-Is-Us has a portfolio of marketable securities that originally cost $19,000. As of December 31, the market value of these securities was $27,500. All short-term investments are classified as “available for sale.”
3. During December, $6,400 of accounts receivable were written off as uncollectible. A recent aging of the company’s accounts receivable led management to conclude that an allowance for doubtful accounts of $8,500 is needed at December 31, 2015.
4. The company uses a perpetual inventory system. A year-end physical count revealed that several guitars reported in the inventory records were missing. The cost of the missing units amounted to $1,350. This amount is not considered significant relative to the total cost of inventory on hand.
5. At December 31, approximately $900 in office supplies remained on hand.
6. The company pays for its insurance policies 12 months in advance. Its most recent payment was made on November 1, 2015. The cost of this policy was slightly higher than the cost of coverage for the previous 12 months.
7. Depreciation expense related to the company’s building and fixtures is $5,000 for the month ending December 31, 2015.
8. Although Music-Is-Us carries an extensive inventory, it is not uncommon for experienced musicians to order custom guitars made to their exact specifications. Manufacturers do not allow any sales returns of custom-made guitars. The entire sales amount is collected at the time a custom order is placed, and is credited to an account entitled “Unearned Customer Deposits.” As of December 31, $4,800 of these deposits remained unfilled because the special-order guitars have not been received from the manufacturer. The cost of goods sold and the reduction in inventory associated with all custom orders is recorded when the custom merchandise is delivered to customers. At that time, the adjusting entry requires only a decrease to unearned customer deposits and an increase in sales.
9. Accrued income taxes payable for the entire year ending December 31, 2015, total $81,000. No income tax payments are due until early in 2016.
Instructions
a. Prepare a bank reconciliation and make the journal entries to update the accounting records of Music-Is-Us as of December 31, 2015.
b. Prepare the adjusting entry to update the company’s marketable securities portfolio to its mark-to-market value.
c. Prepare the adjusting entry at December 31, 2015, to report the company’s accounts receivable at their net realizable value.
d. Prepare the entry to account for the guitars missing from the company’s inventory at the end of the year.
e. Prepare the adjusting entry to account for the office supplies used during December.
f. Prepare the adjusting entry to account for the expiration of the company’s insurance policies during December.
g. Prepare the adjusting entry to account for the depreciation of the company’s building and fixtures during December.
h. Prepare the adjusting entry to report the portion of unearned customer deposits that were earned during December.
i. Prepare the adjusting entry to account for income tax expense that accrued during December.
j. On the basis of the adjustments made to the accounting records in parts a through i above, prepare the company’s adjusted trial balance at December 31, 2015.
k. Using the adjusted trial balance prepared in part j above, prepare an annual income statement, statement of retained earnings, and a balance sheet dated December 31, 2015.
l. Using the financial statements prepared in part k above, determine approximately how many days on average an account receivable remains outstanding before it is collected. You may assume that the company’s ending accounts receivable balance on December 31 is a close approximation of its average accounts receivable balance throughout the year.
m. Using the financial statements prepared in part k, determine approximately how many days on average an item of merchandise remains in stock before it is sold. You may assume that the company’s ending merchandise inventory balance on December 31 is a close approximation of its average merchandise inventory balance throughout the year.
n. Using the financial statements prepared in part k, determine approximately how many days it takes to convert the company’s inventory into cash. In other words, what is the length of the company’s operating cycle?
o. Comment briefly upon the company’s financial condition from the perspective of a short-term creditor.
Step by Step Answer:

Financial and Managerial Accounting the basis for business decisions
ISBN: 978-0078025778
17th edition
Authors: Jan Williams, Susan Haka, Mark Bettner, Joseph Carcello





