Question: Consider the following one-dimensional problem: This is a concave problem, since the leading term in the quadratic objective is negative, so that the second-order derivative
Consider the following one-dimensional problem:
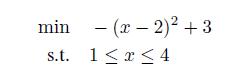
This is a concave problem, since the leading term in the quadratic objective is negative, so that the second-order derivative is negative everywhere. In Fig. 15.5, we show the objective function and the feasible set. The stationarity point x = 2 is of no use to us, since it is a maximizer. We see that local minimizers are located at the boundary of the feasible set. A local minimizer lies at the left boundary, x = 1, and the global minimizer is located at the right boundary, x = 4.
Data From Fig 15.5
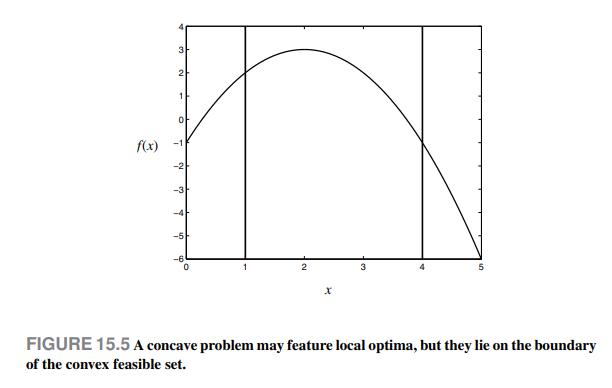
min (x-2)+3 s.t. 1 <
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (181 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


