Question: As discussed in the chapter, abnormal earnings (AE) are AE t = X t (r e BV t 1 ) where X t is
As discussed in the chapter, abnormal earnings (AE) are
AEt = Xt − (re × BVt−1)
where Xt is the firm’s net income, re is the cost of equity capital, and BVt–1 is the book value of equity at t − 1.
Following are Xt, BVt–1, and re for two firms.
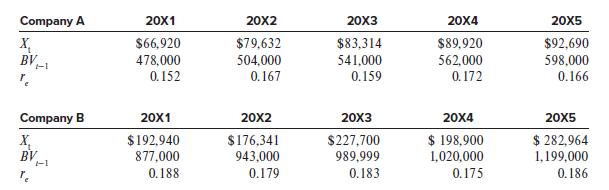
Required:
1. Calculate each firm’s AEt each year from 20X1 to 20X5.
2. Which firm was better managed over the 20X1–20X5 period? Why?
3. Which firm is likely to be the better stock investment in 20X6 and beyond? Why?
Company A 20X1 20X2 203 20X4 20X5 X BV $6,920 $79,632 $83,314 $89,920 $92,690 478,000 0.152 504,000 541,000 0.159 562,000 598,000 0.167 0. 172 0.166 Company B 20X1 20X2 203 20X4 20X5 X BV $192,940 877,000 0.188 $176,341 943,000 $227,700 989,999 0.183 $ 198,900 1,020,000 $ 282,964 1,199,000 0.179 0.175 0.186
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Requirement 1 The abnormal earnings of the two firms for 20X120X7 appear below Company A 20X1 20X2 20X3 20X4 20X5 X t 66920 79632 83314 89920 92690 BV ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


