Question: (a) Suppose a projectile is launched vertically from the surface r = R of the earth with initial velocity v 0 = 2GM/R, so v
(a) Suppose a projectile is launched vertically from the surface r = R of the earth with initial velocity v0 = √2GM/R, so v20 = k2/R where k2 = 2GM. Solve the differential equation dr/dt = k/√r (from Eq. (23) in this section) explicitly to deduce that r(t) → ∞ as t → ∞.
(b) If the projectile is launched vertically with initial velocity v0 > √2GM/R, deduce that
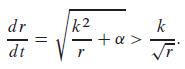
Why does it again follow that r(t) → ∞ as t → ∞?
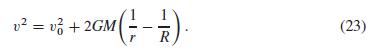
dr R dt k2 ta> k F
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a b Therefore at every instant in its ascent the upward v... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


