Question: Problems 43 through 46 concern the differential equation where k is a constant. Suppose the velocity v of a motorboat coasting in water satisfies the
Problems 43 through 46 concern the differential equation
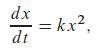
where k is a constant.
Suppose the velocity v of a motorboat coasting in water satisfies the differential equation dv/dt = kv2. The initial speed of the motorboat is v(0) = 10 meters per second (m/s), and v is decreasing at the rate of 1 m/s2 when v = 5 m/s. Based on the result of Problem 43, long does it take for the velocity of the boat to decrease to 1 m/s? To 1/10m/s? When does the boat come to a stop?
dx dt = kx2,
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (172 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Substitution of v 1 and v 5 into the differential equation v kv 2 gives k 125 so Problem ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


