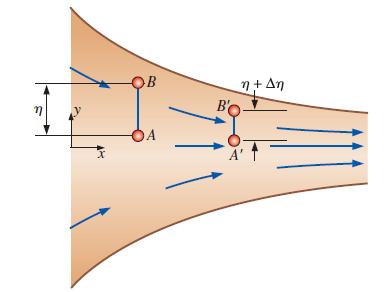
Question: Converging duct flow is modeled by the steady, two dimensional velocity field of Prob. 417. As vertical line segment AB moves downstream it shrinks from
Converging duct flow is modeled by the steady, two dimensional velocity field of Prob. 4–17. As vertical line segment AB moves downstream it shrinks from length η to length η + Δη as sketched in Fig. P4–55. Generate an analytical expression for the change in length of the line segment, Δη. Note that the change in length, Δη, is negative.
Data from Problem 4-17.
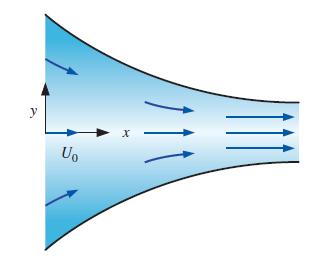
Consider steady, incompressible, two-dimensional flow through a converging duct (Fig. P4–17). A simple approximate velocity field for this flow is
![]()
where U0 is the horizontal speed at x = 0. Note that this equation ignores viscous effects along the walls but is a reasonable approximation throughout the majority of the flow field. Calculate the material acceleration for fluid particles passing through this duct. Give your answer in two ways:
(1) As acceleration components ax and ay
(2) As acceleration vector a(vector)
n OA 3,+ An B'O
Step by Step Solution
3.52 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


