Question: Repeat Example 917, except for the case in which the wall is inclined at angle (Fig. P993). Generate expressions for both the pressure and
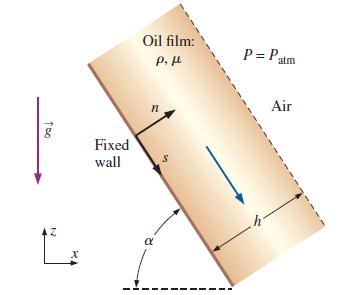
Repeat Example 9–17, except for the case in which the wall is inclined at angle α (Fig. P9–93). Generate expressions for both the pressure and velocity fields. As a check, make sure that your result agrees with that of Example 9–17 when α = 90°. [It is most convenient to use the (s, y, n) coordinate system with velocity components (us, v, un), where y is into the page in Fig. P9–93. Plot the dimensionless velocity profile us* versus n* for the case in which α = 60°.]
FIGURE P9–93
Data from Example 9-17
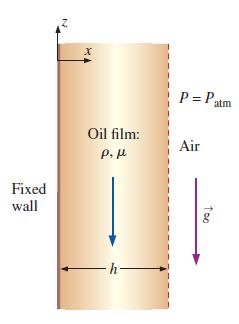
Consider steady, incompressible, parallel, laminar flow of a film of oil falling slowly down an infinite vertical wall (Fig. 9–68). The oil film thickness is h, and gravity acts in the negative z-direction (downward in Fig. 9–68). There is no applied (forced) pressure driving the flow—the oil falls by gravity alone. Calculate the velocity and pressure fields in the oil film and sketch the normalized velocity profile. You may neglect changes in the hydrostatic pressure of the surrounding air.
FIGURE 9–68
| too N X Fixed wall Oil film: P. n P = Patm Air
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


