Question: Refer to Example 23-2. Select a reducing agent (from Table 23.1 or Appendix D) that will reduce VO 2+ to V 3+ and no further
Refer to Example 23-2. Select a reducing agent (from Table 23.1 or Appendix D) that will reduce VO2+ to V3+ and no further in acidic solution.
Example 23-2
Can MnO4–(aq) be used to oxidize VO2+(aq) to VO2+(aq) for standard-state conditions in an acidic solution? If so, write a balanced equation for the redox reaction.
Table 23.1
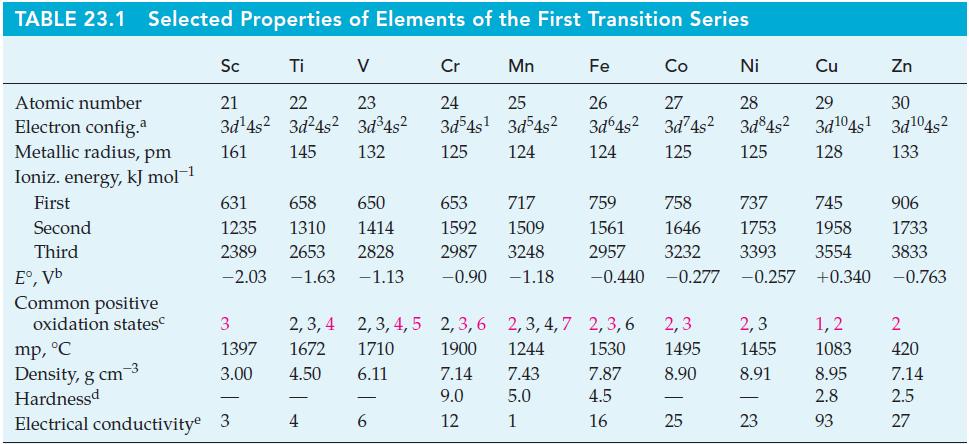
TABLE 23.1 Selected Properties of Elements of the First Transition Series Atomic number Electron config.a Metallic radius, pm Ioniz. energy, kJ mol-1 First Second Third E,Vb Common positive oxidation states Sc Ti V 21 22 3d4s 3d4s 161 145 3 1397 3.00 mp, C Density, g cm-3 Hardnessd Electrical conductivity 3 23 3d4s 132 631 658 650 653 717 1235 1414 1592 1509 1310 2389 2653 2828 2987 3248 -2.03 -1.63 -1.13 -0.90 -1.18 2,3,4 2,3,4,5 1672 1710 4.50 6.11 4 Cr 24 3d4s 125 6 Mn 25 3d54s 124 Fe Co 26 27 3d64s 3d74s 124 125 Ni 28 3d84s 125 759 758 737 745 906 1646 1753 1958 1733 1561 2957 3232 3393 3554 3833 -0.440 -0.277 -0.257 +0.340 -0.763 2,3,6 2,3,4,7 2,3,6 2,3 2,3 1900 1244 1530 1495 1455 7.14 7.43 7.87 8.90 8.91 9.0 5.0 4.5 12 1 16 25 - Cu Zn 29 30 3d04s 3d04s 128 133 23 1,2 1083 8.95 2.8 93 2 420 7.14 2.5 27
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Reducing agent Zn Balanced equation VO2aq Zns 2 Haq V3aq Zn2aq H2Ol Zn is a go... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


