Consider the packed bed operating conditions of Problem 5.13, but with Pyrex ( (ho=2225 mathrm{~kg} / mathrm{m}^{3},
Question:
Consider the packed bed operating conditions of Problem 5.13, but with Pyrex ( \(ho=2225 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}, c=835 \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{kg} \cdot \mathrm{K}\), \(k=1.4 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m} \cdot \mathrm{K}\) ) used instead of aluminum. How long does it take a sphere near the inlet of the system to accumulate \(90 \%\) of the maximum possible thermal energy? What is the corresponding temperature at the center of the sphere?
Data From Problem 5.13:-
Thermal energy storage systems commonly involve a packed bed of solid spheres, through which a hot gas flows if the system is being charged, or a cold gas if it is being discharged. In a charging process, heat transfer from the hot gas increases thermal energy stored within the colder spheres; during discharge, the stored energy decreases as heat is transferred from the warmer spheres to the cooler gas.
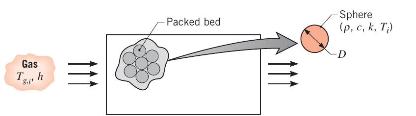
Consider a packed bed of 75-mm-diameter aluminum spheres \(\left(ho=2700 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}, c=950 \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{kg} \cdot \mathrm{K}, k=240\right.\) \(\mathrm{W} / \mathrm{m} \cdot \mathrm{K}\) ) and a charging process for which gas enters the storage unit at a temperature of \(T_{g, i}=300^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). If the initial temperature of the spheres is \(T_{i}=25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and the convection coefficient is \(h=75 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m}^{2} \cdot \mathrm{K}\), how long does it take a sphere near the inlet of the system to accumulate \(90 \%\) of the maximum possible thermal energy? What is the corresponding temperature at the center of the sphere? Is there any advantage to using copper instead of aluminum?
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781119220442
8th Edition
Authors: Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine





