Question: Thermal energy storage systems commonly involve a packed bed of solid spheres, through which a hot gas flows if the system is being charged, or
Thermal energy storage systems commonly involve a packed bed of solid spheres, through which a hot gas flows if the system is being charged, or a cold gas if it is being discharged. In a charging process, heat transfer from the hot gas increases thermal energy stored within the colder spheres: during discharge, the stored energy decreases as heat is transferred from the warmer spheres to the cooler gas.
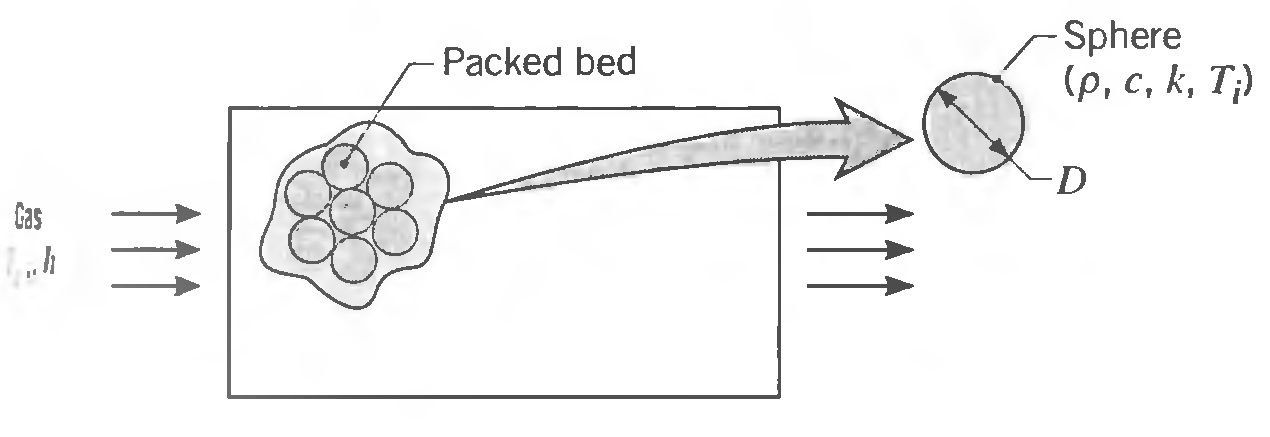
Consider a packed bed of 75-mm-diameter aluminum spheres (p = 2700 kg/m3 ∙ c = 950 J/kg ∙ K, k = 240 W/m ∙ K) and a charging process for which gas enters the storage unit at a temperature of Tg,i = 300°C. If the initial temperature of the spheres is Tj = 25°C and the convection coefficient is h = 75 W/m2 ∙ K, how long does it take a sphere near the inlet of the system to accumulate 90% of the maximum possible thermal energy? What is the corresponding temperature at the center of the sphere? Is there any advantage to using copper instead of aluminum?
Sphere (p, c, k, T;) Packed bed Gas
Step by Step Solution
3.37 Rating (175 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
KNOWN Diameter density specific heat and thermal conductivity of aluminum spheres used in packed bed ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
8-E-M-E-H-M-T (373).docx
120 KBs Word File


