For continuous distillation of a binary mixture of constant relative volatility, the minimum reflux ratio can be
Question:
For continuous distillation of a binary mixture of constant relative volatility, the minimum reflux ratio can be determined analytically from the following equation (Treybal, 1980):
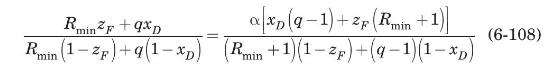
Use (6-108) to estimate \(R_{\min }\) for distillation of the benzene-toluene mixture of Example 6.4. Assume that, for this system at \(1 \mathrm{~atm}\), the relative volatility is constant at \(\alpha=2.5\).
Data From Example 6.4:-
A trayed tower operating at 1 atm is to be designed to continuously distill 200 kmol/h (55.6 mol/s) of a binary mixture of 60 mol% benzene, 40 mol% toluene. A liquid distillate and a liquid bottoms product of 95 mol% and 5 mol% benzene, respectively, are to be produced. Before entering the column, the feed—originally at 298 K—is flash-vaporized at 1 atm to produce an equimolal vapor–liquid mixture (VF/F = LF/F = 0.5). A reflux ratio 30% above the minimum is specified. Calculate:
(a) quantity of the products;
(b) minimum number of theoretical stages, Nmin;
(c) minimum reflux ratio;
(d) number of equilibrium stages and the optimal location of the feed stage for the reflux ratio specified; and
(e) thermal load of the condenser, reboiler, and feed preheater.
Equation 6-108:-
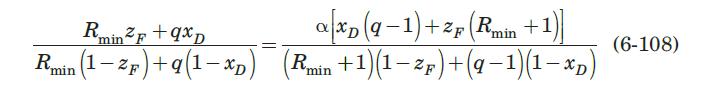
Step by Step Answer:






