Question: Since leaf nodes require no pointers to children, they could conceivably use a different (larger) t value than internal nodes for the same disk page
Since leaf nodes require no pointers to children, they could conceivably use a different (larger) t value than internal nodes for the same disk page size. Show how to modify the procedures for creating and inserting into a B-tree to handle this variation.
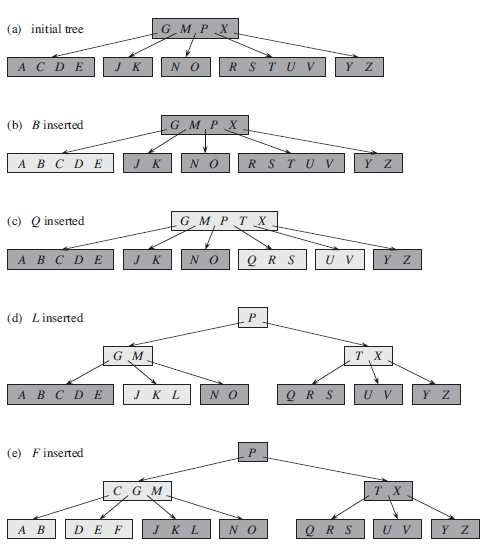
Figure 18.7 Inserting keys into a B-tree. The minimum degree t for this B-tree is 3, so a node can hold at most 5 keys. Nodes that are modified by the insertion process are lightly shaded. (a) The initial tree for this example. (b) The result of inserting B into the initial tree; this is a simple insertion into a leaf node. (c) The result of inserting Q into the previous tree. The node RST UV splits into two nodes containing RS and UV , the key T moves up to the root, and Q is inserted in the leftmost of the two halves (the RS node). (d) The result of inserting L into the previous tree. The root splits right away, since it is full, and the B-tree grows in height by one. Then L is inserted into the leaf containing JK. (e) The result of inserting F into the previous tree. The node ABCDE splits before F is inserted into the rightmost of the two halves (the DE node).
(a) initial tree GM, P X AC DE R STUV JK N O Y Z (b) Binserted GM,P X A B C DE R S T U V JK N O Y Z (c) Q inserted GM PT X A B C DE J K N O Q R S U V Y Z (d) Linserted G M T X A B C DE JK L QR S U V Y Z N O (e) Finserted |C G M T X A B JK L N O Q R S U V Y Z DE F
Step by Step Solution
3.34 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To handle different t values for leaf and internal nodes in a Btree we need to modify the procedures ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


