Schulte et al. discuss a linear solvation energy relationship (LSER) method for the partitioning of 41 environmentally
Question:
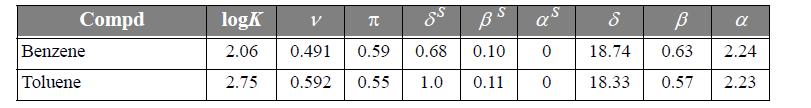
Schulte et al. discuss a linear solvation energy relationship (LSER) method for the partitioning of 41 environmentally important compounds between hexane + water phases at 25°C. The LSER method is based on the idea that contributions to the Gibbs excess energy (and to the logarithm of the partition coefficient) from effects like van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonding are independent of each other. Therefore, these contributions can be added up as separate linear contributions. We can test this hypothesis by plotting partition data for several compounds based on experimental data and LSER. We can also test the predictive capabilities of alternative theories by plotting their results with different curves. Table 14.2 presents the required parameters for the LSER method for several compounds.
These parameters are to be substituted into the equation: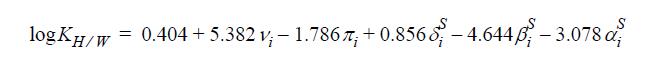
where ν = volume parameter, π = polarity parameter, δS = polarizability parameter, βS = hydrogen bond acceptor parameter, and α = hydrogen bond donor parameter. Compute the log partition coefficients for the following compounds by the LSER method and plot them against the experimental values listed in Table 14.2. Include predictions using the following methods.
(a) The MAB model.
(b) The SSCED model.
(c) The UNIFAC model.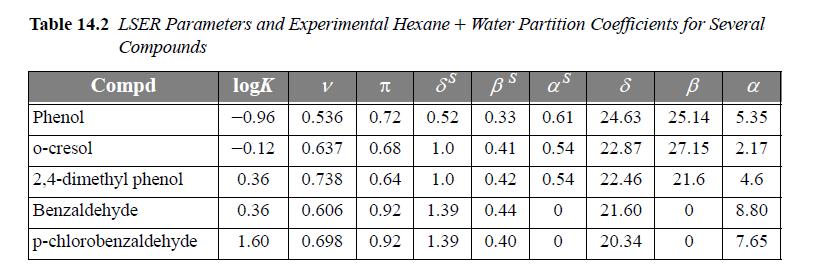
Step by Step Answer:

Introductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9780136068549
2nd Edition
Authors: J. Elliott, Carl Lira





