Question: Letting X denote the random variable that is defined as the sum of two fair dice, then In other words, the random variable X can
Letting X denote the random variable that is defined as the sum of two fair dice, then
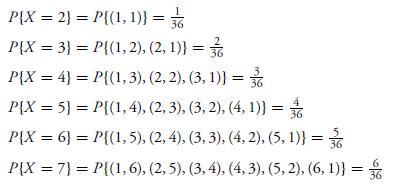
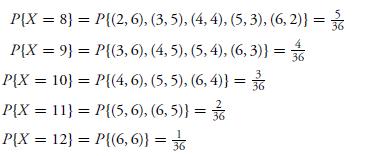
In other words, the random variable X can take on any integral value between 2 and 12 and the probability that it takes on each value is given by Equation 4.1.1. Since X must take on some value, we must have
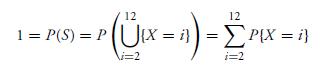
which is easily verified from Equation 4.1.1.
Another random variable of possible interest in this experiment is the value of the first die. Letting Y denote this random variable, then Y is equally likely to take on any of the values 1 through 6. That is, P{Y = i} = 1/6, i = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
P{X=2} = P{(1, 1)} = P{X=3} = P{(1, 2), (2, 1)) = P{X = 4} = P{(1, 3), (2, 2), (3, 1)} = 36 P{X=5} = P{(1, 4), (2, 3), (3, 2), (4, 1)) = P{X = 6} = P{(1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 3), (4, 2), (5, 1)} = 36 P{X = 7} = P{(1, 6), (2, 5), (3, 4), (4, 3), (5, 2), (6, 1)} = 36
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


