Question: Assume an ordinary queue has been declared with the Queue interface and instantiated with the ArrayDeque class. Also, assume a priority queue has been declared
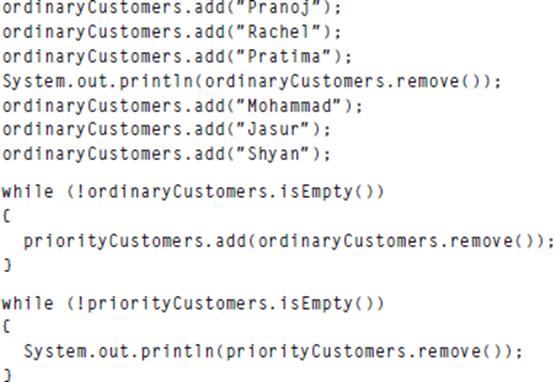
Assume an ordinary queue has been declared with the Queue interface and instantiated with the ArrayDeque class. Also, assume a priority queue has been declared with the Queue interface and instantiated with the PriorityQueue class. Figure 10.15 shows that the PriorityQueue class also implements the Queue interface. Therefore, the PriorityQueue class also implements add and remove methods. Its remove method does the same thing as ArrayDeque’s remove method. But its add method is different. When it adds elements, a priority queue inserts them into the queue so that lower-valued elements are always closer to the front. In other words, in a priority queue, lower-valued elements have priority and “crash” the line. Given this understanding, show the output produced by the following code fragment:
You should be able to do this by just thinking about it, but feel free to complete and run a program to check your answer.
ordinary Customers.add("Pranoj"); ordinary Customers.add("Rachel"); ordinary Customers.add("Pratima"); System.out.println(ordinary Customers.remove()); ordinary Customers.add("Mohammad"); ordinary Customers.add("Jasur"); ordinary Customers.add("Shyan" ); while (!ordinary Customers.isEmpty()) ( priority Customers.add(ordinary Customers.remove()); } while (!priority Customers.isEmpty()) { System.out.println(priority Customers.remove());
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The code snippet youve provided is incomplete but from what I can see its demonstrating the function of a standard queue operated through an ArrayDequ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


