Question: Our linked-list class allowed insertions and deletions at only the front and the back of the linked list. These capabilities were convenient for us when
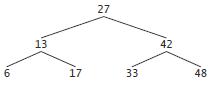
Our linked-list class allowed insertions and deletions at only the front and the back of the linked list. These capabilities were convenient for us when we used composition to produce a stack class and a queue class with minimal code simply by reusing the list class. Linked lists are normally more general than those we provided. Modify the linked-list class we developed in this chapter to handle insertions and deletions anywhere in the list. Create diagrams comparable to Figs. 21.5 (insertAtFront), 21.6 (insertAtBack), 21.7 (removeFromFront) and 21.8 (removeFromBack) that show how to insert a new node in the middle of a linked list and how to remove an existing node from the middle of a linked list.
Figs. 21.5
Figs. 21.6
Figs. 21.7
Figs. 21.8
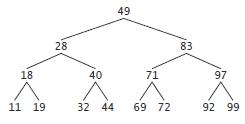
I // Fig. 21.15: Tree.java 2 // TreeNode and Tree class declarations for a binary search tree. 3 package com.deitel.datastructures; 4 5 // class TreeNode definition 6 class TreeNode { 7 8 9 10 IL 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 } 42 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 // package access members TreeNode leftNode; 99 100 101 } E data; // node value TreeNode rightNode; // constructor initializes data and makes this a leaf node public TreeNode (E nodeData) { data nodeData; leftNode= rightNode = null; // node has no children } // locate insertion point and insert new node; ignore duplicate values public void insert(E insertValue) { // insert in left subtree } if (insertValue.compareTo (data) < 0) { // insert new TreeNode } } if (leftNode == nul1) { leftNode= new TreeNode (insertValue); } else { // continue traversing left subtree recursively leftNode.insert(insertValue); } // insert in right subtree else if (insert Value.compareTo (data) > 0) { // class Tree definition public class Tree { private TreeNode root; } // constructor initializes an empty Tree of integers public Tree() {root = null;} //insert new TreeNode. if (rightNode == nu11) { rightNode = new TreeNode (insertValue); } else { // continue traversing right subtree recursively rightNode.insert(insertValue); } // insert a new node in the binary search tree public void insertNode (E insertValue) { if (root == null) { root = new TreeNode (insertValue); // create root node } } } else { root.insert(insertValue); // call the insert method // begin preorder traversal public void preorderTraversal() {preorderHelper (root); } // recursive method to perform preorder traversal private void preorderHelper (TreeNode node) { if (node == null) { return; } System.out.printf("%s", node.data); // output node data preorderHelper (node.leftNode); // traverse left subtree preorderHelper(node.rightNode); // traverse right subtree } // begin inorder traversal public void inorder Traversal() {inorderHelper(root); } // recursive method to perform inorder traversal private void inorderHelper (TreeNode node) { if (node == nu11) { return; } inorderHelper (node.leftNode); // traverse left subtree System.out.printf( "%s ", node.data); // output node data inorderHelper (node.rightNode); // traverse right subtree } // begin postorder traversal public void postorderTraversal() [postorderHelper (root); } // recursive method to perform postorder traversal private void postorderHelper (TreeNode node) { if (node =null) { return; } postorderHelper (node.leftNode); // traverse left subtree postorderHelper (node.rightNode); // traverse right subtree System.out.printf("%s", node.data); // output node data
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Heres the modified linkedlist class Insertion in the middle ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


