On January 1, Year 8, Panet Company acquired 40,000 common shares of Saffer Corporation, a public company,
Question:
On January 1, Year 8, Panet Company acquired 40,000 common shares of Saffer Corporation, a public company, for $500,000. This purchase represented 8% of the outstanding shares of Saffer. It was the intention of Panet to acquire more shares in the future in order to eventually gain control of Saffer.
On January 1, Year 10, Panet purchased an additional 135,000 common shares of Saffer for $1,890,000. Saffer's shareholders' equity section was as follows:

On this date, the fair values of Saffer's assets were equal to carrying amounts, except for inventory, which was undervalued by $120,000, and land, which was undervalued by $1,000,000.
On January 1, Year 11, Panet purchased an additional 225,000 common shares of Saffer for $3,600,000. Saffer's shares were trading on the open market for $15 per share on the date of acquisition. The shareholders' equity section for Saffer was as follows:

On January 1, Year 11, the fair values of Saffer's assets were equal to carrying amounts except for the following:

The plant and equipment had a remaining useful life of 20 years. The long-term liabilities mature on December 31, Year 20.
The balance sheets as at December 31, Year 12, and the income statements for the year ending December 31, Year 12, for the two companies are as follows:
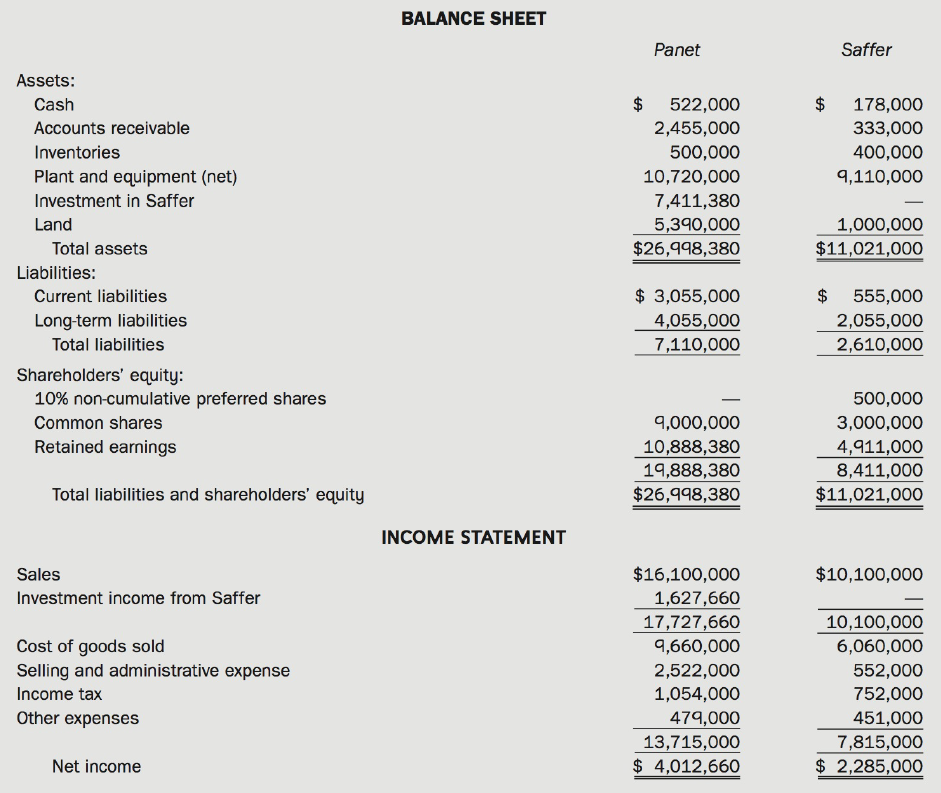
Additional Information:
• Dividends declared and paid during Year 12:
Panel $500,000
Saffer 250,000
• On January 1, Year 12, the inventory of Panet contained a $107,000 intercompany profit, and the inventory of Saffer contained an intercompany profit amounting to $157,000.
• During Year 12, Saffer sold inventory to Panet for $3,200,000 at a gross profit margin of 35%. Sales of $400,000 remained in Panet's inventory at December 31, Year 12.
• During Year 12, Panet sold inventory to Saffer for $2,800,000 at a gross profit margin of 45%. Sales of $250,000 remained in Saffer's inventory at December 31, Year 12.
• Saffer sold a piece of equipment to Panet on July 1, Year 12, for $560,000. At that time, the carrying amount of the equipment in Saffer's books was $350,000, and it had a remaining useful life of 10.5 years. Panet still owes Saffer for 30% of the purchase price of the equipment. The gain on sale has been netted against other expenses in Saffer's Year 12 income statement.
• Panet uses the eq_uity method to account for its investment in Saffer. Both companies follow the straight-line method for depreciating plant and eq_uipment, and for premiums or discounts on long-term liabilities.
• A goodwill impairment loss of $103,000 was recorded in Year 11, and a further loss of $69,000 occurred in Year 12. The impairment losses are to be applied at 80% to Panet's shareholders and 20% to non-controlling interest.
• Depreciation expense is included with selling and administrative expenses, whereas goodwill impairment losses are included in other expenses.
• Assume a 40% tax rate.
Required:
(a) Prepare the following Year 12 consolidated financial statements:
(i) Income statement
(ii) Balance sheet
(b) Calculate goodwill impairment loss and non-controlling interest on the consolidated income statement for the year ended December 31, Year 12, under parent company extension theory.
(c) lf Panet had used parent company extension theory rather than entity theory, how would this affect the debt-to-equity ratio at the end of Year 12?
(d) Prepare the consolidated financial statements using the worksheet approach.
GoodwillGoodwill is an important concept and terminology in accounting which means good reputation. The word goodwill is used at various places in accounting but it is recognized only at the time of a business combination. There are generally two types of... Financial Statements
Financial statements are the standardized formats to present the financial information related to a business or an organization for its users. Financial statements contain the historical information as well as current period’s financial... Consolidated Income Statement
When talking about the group financial statements the consolidated financial statements include Consolidated Income Statement that a parent must prepare among other sets of consolidated financial statements. Consolidated Income statement that is...
Step by Step Answer:

Modern Advanced Accounting in Canada
ISBN: 978-1259087554
8th edition
Authors: Hilton Murray, Herauf Darrell





